
4 Important Reasons Contract Standards Fail and 10 Practical Solutions
Contracts – for example Master Services Agreements, Customer Agreement or Terms & Conditions – are the backbone of virtually every business transaction. The best way to have the signing process run smoothly is by using contract templates.
For example, for all these professionals, contracts are an essential part of their work:
- a sales professional sealing a new deal;
- an entrepreneur looking for funding;
- a procurement specialist involved in the negotiation of vendor contracts; or
- a legal professional tasked with protecting company interests
By clearly outlining terms, responsibilities, and expectations, great contracts build trust, mitigate risks and keep business relationships running smoothly.
However, contracts can also become a source of complexity. Many companies desire that a new product, service, or partnership requires its own unique contract language. This can quickly turn into an administrative and legal bottleneck if not managed properly. This is why smart organizations turn to contract templates. When thoughtfully designed and regularly updated, these templates streamline contract creation and negotiation, saving both time and resources.
Contract templates are only as good as the process behind them. If they’re too long, packed with dense legal jargon, or buried in a repository that nobody can find, even the most well-written templates won’t make a difference. That’s where this article series comes in. It will help you craft contract templates that really accelerate deals while protecting your organization’s interests. We will first start with the ‘Most Important Reasons Contract Standards Fail and Practical Solutions’.
What We Will Cover
In this introductory article, we will explore the value of using contract templates and highlight key pitfalls that can undermine them. We will then examine the potential consequences of poorly managed templates and, finally, demonstrate the benefits your business can gain by developing modern, easy-to-use contract templates.
Here’s a quick overview of what you can expect:
- Why We Need (Better) Contract Templates
We’ll discuss why organizations of all sizes and industries should focus on improving their templates. Examples will range from standard Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) to specialized industry contracts like AI software licensing or wind turbine supply agreements. - Common Issues with Contract Templates
We’ll identify the biggest challenges that derail template usage, from outdated clauses to complicated language that sales teams struggle to understand. - Consequences of Contract Template Issues
We’ll look at how these problems can delay deals, increase risk, and strain business relationships. - Results of Having State-of-the-Art Templates
We’ll highlight the positive impact of streamlined, clearly written, and easily accessible templates—such as faster negotiations and reduced legal bottlenecks. - Real Life Examples of Contract Optimization
- How to Improve Your Contract Standards & Templates
We’ll draw on two decades of professional insights into how companies achieve the best outcomes and keep improving their contracts over time.
This article sets the stage. The upcoming series of articles, called “10 Tips You Need to Know to Improve Your Contract Templates,” will dive deeper into each tip – see below the full list of tips. This will offer you practical steps to help you develop contract templates that truly serve your business. Before we get there, let’s start by laying out why a solid set of templates is indispensable—and where most organizations go wrong.
Why We Need (Better) Contract Templates
Organizations often juggle a wide range of agreements, from the simplest Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) to the most complexTerms & Conditions or Master Services Agreement (MSA). Companies, for instance, often deal with Software as a Service (SaaS) contracts (Salesforce, ServiceNow, HubSpot). Each contract type can be drastically different, but they all share one objective: to clearly outline obligations, manage expectations and mitigate risk.
Balancing Clarity and Complexity
One of the main reasons companies need better contract templates is the tension between clarity and complexity. A good contract should be thorough enough to protect the business while still being concise and straightforward. For example, a wind turbine manufacturer might need clauses that cover equipment specifications, maintenance, installation timelines, and environmental compliance. Adding too many layers of complex legal text, however, can slow negotiations or make the contract inaccessible for non-legal stakeholders.
By creating well-structured, user-friendly templates, you ensure that each new contract iteration doesn’t require a complete rewrite. Instead, your teams can modify or append specific clauses to tailor the template to each deal, project, or relationship. This level of uniformity can dramatically cut down on drafting time, reduce back-and-forth with legal counsel, and speed up the signature process.
Enhancing Workflows
Well-designed templates also improve workflows by establishing a clear starting point. If you are repeatedly negotiating Master Services Agreements or Terms & Conditions (T&Cs), for instance, you want your sales or procurement colleagues to know exactly which clauses are standard and which ones might need special approval. This clarity keeps deals moving quickly and prevents confusion.
In a tech environment, especially one dealing with SaaS or AI solutions, the speed of execution can be a competitive advantage. Having strong, approved templates means your product or service can get to market faster, since you won’t have to battle the same legal issues repeatedly.
Keeping Pace with Evolving Business Needs
Business models evolve rapidly. Just think about how quickly AI technology is reshaping industries or how sustainability concerns are driving new contract requirements for wind turbine manufacturers. If your contracts don’t keep up with these changes, you could end up with agreements that fail to address emerging risks or market demands. For example, an AI contract might need robust clauses related to data privacy, algorithmic bias, or intellectual property ownership.
Templates need regular updates to accommodate new legal requirements, shifts in company strategy, and lessons learned from recent deals. Far too often, companies let their templates gather dust, failing to reflect current regulations, technology changes, or internal processes. This is why dedicating resources to regularly refining and updating templates isn’t a luxury—it’s a necessity for any forward-thinking enterprise.
Common Issues with Contract Templates
Despite their obvious advantages, contract templates can become more of a hindrance than a help if they aren’t properly managed. Below are four issues that commonly arise.
1. Complexity
Overly long, technical, or legalistic language can deter people from using templates. A contract for a wind turbine supply project, for example, might run dozens of pages, filled with specialized engineering terms. If the language is too arcane, the sales or operations team might avoid the template altogether, reverting to manual drafting or older versions. This reduces consistency and can create legal blind spots.
2. Accessibility
Just having great templates on file doesn’t help anyone if they can’t be found. Many organizations store templates in multiple folders or on different file-sharing platforms without clear naming conventions. This leads to confusion, version control issues, and the risk of using outdated documents.
3. Limited Resources
Template management can fall by the wayside when legal teams are stretched thin. With pressing demands like regulatory compliance, litigation, or high-stakes contract negotiations, dedicating time to reviewing and updating templates can seem like a low priority. As a result, templates quickly become outdated or overlooked.
4. Excessive Legal Review
One main benefit of templates is the reduction of legal review times—yet this only works if the templates are well-structured and widely trusted. If internal stakeholders distrust a template’s accuracy, they’ll still funnel contracts to Legal for a deep dive. When every single deal, even small ones, becomes a bottleneck, it defeats the entire purpose of having a standardized approach.
Consequences of Contract Template Issues
Neglecting contract templates or managing them poorly can trigger a cascade of problems:
Delays in Contract Creation, Negotiation and Signing
If a template is unwieldy or unclear, it can’t speed up much of anything. Negotiations might stall as both parties parse through unnecessary terms or loop in legal counsel for clarifications. In fast-paced markets like AI or SaaS solutions, a few weeks’ delay can mean lost opportunities.
Increased Risk Exposure
Templates are supposed to protect the company from legal pitfalls, but if they’re outdated or inconsistent, they can introduce more risk. For instance, imagine you’re finalizing a wind turbine maintenance contract and your template lacks a recent clause covering environmental regulations. You could face unforeseen liabilities or compliance issues if something goes wrong.
Higher Workloads
Legal, procurement, and sales teams spend far more time dealing with avoidable contract snags when templates aren’t user-friendly. Instead of focusing on strategic deals or high-risk situations, experienced counsel and managers waste hours revising the same clauses because the existing template is missing critical updates.
Strained Business Relationships
Contracts serve as touchpoints of trust and efficiency. Clients or partners who encounter errors, inconsistencies, or long delays may question your professionalism. This can harm relationships, with ripple effects on future collaborations and your reputation in the market.
Results of Having State-of-the-Art Templates
When companies invest in robust, well-maintained contract templates, the benefits are felt across every stage of the deal cycle. Below are nine advantages you can expect when you get it right:
1. Shorter Contract Negotiation Times
With standard terms already approved, you avoid renegotiating common clauses for each new agreement. Whether you’re drawing up a SaaS user agreement, an AI licensing contract, or an extensive MSA for wind turbine installations, both sides can focus on the unique aspects of the deal instead of wading through boilerplate clauses.
2. Increased Efficiency and Simplified Contract Handling
Well-organized templates reduce repetitive drafting. This frees up your legal, sales, and procurement teams to concentrate on more strategic tasks—like market expansion, major partnerships, or regulatory shifts that impact your industry. In tech, efficiency gains can translate directly into faster product launches or new feature rollouts.
3. Reduced Workload
By cutting down on the number of contracts that need an in-depth legal review, you open up bandwidth for high-value activities. This not only alleviates bottlenecks, it also makes the best use of specialized legal expertise. Instead of reviewing basic NDAs or T&Cs, your legal team can focus on, say, negotiating a complex AI data-sharing agreement or advising on regulations for renewable energy installations.
4. Enhanced Consistency and Contract Quality
A consistent, predictable approach builds trust with stakeholders. For instance, if you’re partnering with multiple wind farms, each contract will look and feel similar, providing confidence to partners that you know how to handle regulatory requirements, risk allocations, and maintenance responsibilities.
5. Risk Mitigation
Well-crafted templates function as a built-in risk management tool. By integrating updated clauses on liability, data protection, intellectual property, and compliance, you create a safety net that reduces the likelihood of legal disputes. This is particularly crucial in cutting-edge fields like AI, where regulations are still evolving and clarity is paramount.
6. Decreased Legal Costs & Improved Cost Efficiency
When legal teams spend less time reviewing common contracts, your organization saves money. Those resources can then be reallocated to essential areas—like exploring new tech partnerships or investing in research and development for AI or wind turbine efficiency upgrades.
7. Stronger Business Relationships
A smooth, transparent contracting process fosters goodwill. Clients, suppliers, and partners appreciate clarity and efficiency, and they’re more likely to remain loyal or expand the relationship. In specialized industries, like renewable energy, a reputation for easy, fair contracts can be a powerful competitive edge.
8. Optimized Resources
When contract workflows are streamlined, companies can allocate financial and human capital more effectively. This may mean investing in better contract management software, training employees on best practices, or diverting saved resources into innovation initiatives—such as new AI features or advanced turbine technology.
9. Empowered Commercial Teams
Finally, modern contract templates give sales and procurement teams greater autonomy. They can handle routine deals themselves, thanks to pre-approved language. This sense of empowerment boosts morale and allows these teams to focus on building relationships rather than waiting on legal reviews.
Examples: Experienced Results of Contract Optimization
Drawing on two decades of experience in contract optimization, I’ve seen firsthand how transformative good templates can be.
Technology Company
In one instance, a tech company changed its entire suite of legal documents—ranging from SaaS agreements to T&Cs and NDAs—to align them with new data protection laws. By involving key stakeholders (Legal, Sales, and IT Security) from the start, they created a user-friendly, legally robust set of templates. The outcome was a dramatic reduction in contract negotiation times and fewer escalations to senior management.
Renewable Energy
In another example, a renewable energy firm specializing in wind turbine installation tackled their inconsistent and overly complex MSAs. Their previous templates had caused frequent renegotiations and confusion over maintenance responsibilities. After revamping the templates to remove outdated clauses and clarify roles, the average contract closing time dropped by nearly 40%. Clients noted the improved clarity, leading to stronger partnerships and a significant boost in the firm’s industry reputation.
Bringing It All Together
These examples underscore the value of a collaborative approach to contract optimization. It’s not just a legal project; it’s an organizational endeavor that benefits every department involved in contract-related workflows. Regular feedback loops, where Sales or Procurement teams highlight real-world issues they face during negotiations, can pinpoint areas that need refinement. Legal teams, in turn, can incorporate new regulatory updates or risk mitigation strategies. This cycle of continuous improvement keeps your templates relevant, user-friendly, and aligned with evolving business goals.
How to Avoid These Issues and Reach Better Results?
But how can you avoid these issues and reach the advantages & results we discussed above? Stay tuned for our upcoming posts and articles, where we will dive deeper into practical tactics and step-by-step guidance on developing contract templates that truly work for your business.
Best Practices to Roll Out New Contract Templates
If you’re ready to transform your contracts from a necessary evil into a strategic asset, we’re here to help. Whether your primary focus is tech, AI, or renewable energy, every organization can benefit from more streamlined, flexible, and secure contracts. For further guidance on improving contract templates, managing negotiations, and optimizing related processes, reach out via lowa@amstlegal.com or book an appointment with Robby Reggers here.
Follow Robby Reggers and AMST Legal on LinkedIn to read the updates and long form versions of the following posts & articles on these essential topics:
- Use General Terms & Conditions Where Possible
- How to Introduce & Roll Out New Contract Standards Like a Pro
Ultimate Beneficial Ownership (UBO) Explained – What is it and How to Create a Process That Works
The concept of the Ultimate Beneficial Owner (UBO) has moved from a niche concern to a central element of contracts, compliance and due diligence. Whether you’re advising clients on onboarding new customers, hiring a new law firm, negotiating international contracts, or setting up a new corporate entity, understanding UBO requirements is no longer optional – it’s essential.
Failing to understand and address UBO requirements not only leads to significant financial penalties, reputational damage and even legal action. I have also seen that it can slow down many commercial, financial and legal processes. This article ‘Ultimate Beneficial Ownership (UBO) Explained – What is it and How to Create a Process That Works’ provides practical strategies for navigating UBO disclosure – both when requesting information from others and when providing it yourself.
Executive Summary: The TLDR of UBO Compliance
If you only have a minute, here is what you need to know about UBO & managing beneficial ownership:
- The UBO Full Form: It stands for Ultimate Beneficial Owner.
- The Bottom Line: You must identify the “natural person” (human) at the end of the ownership chain, typically at a 25% threshold.
- Strategic Tool: Use a UBO Structure Chart to simplify complex holding layers. This can cut your onboarding time by up to 40%.
- AI Privacy: Professional tools like Claude (on Team/Enterprise plans) generally protect your data, but always check your SLA before uploading sensitive documents.
- Business Impact: Efficient UBO management is a competitive advantage that prevents deal stalls and builds trust with partners like Booking.com or PVH.
What We Will Cover in the Article Below
In this guide, we break down the complexities of beneficial ownership into actionable steps:
- UBO Definitions & Meaning: A clear breakdown of terms for international and beginner readers.
- Legal Frameworks: A summary of global, EU, and Dutch requirements.
- Visual Strategy: Why a UBO Structure Chart is the most effective way to explain your company.
- Industry Deep-Dives: Where these requirements appear most often and which contracts are affected.
- Implementation Framework: A 5-point system for establishing efficient UBO processes.
- AI & Data Privacy: How to handle sensitive ownership information when using tools like Claude.
UBO Definitions: What These Terms Actually Mean
If you are dealing with international contracts or Dutch compliance, you’ll run into these specific terms. For beginners and international teams, here is a breakdown of the essential vocabulary to help you navigate the requirements.
The UBO Master Terminology List – What do the Terms mean that are commonly used?
- UBO Full Form: This stands for Ultimate Beneficial Owner.
- UBO Meaning: This is the “natural person” (a human being) who truly owns or controls a company. Even if the official paperwork lists other companies, the UBO is the person at the end of the line.
- Natural Person: In legal and compliance terms, this just means a human. A UBO can never be another company; it must be a person.
- Pseudo-UBO: If no one person owns enough of the company to be a UBO, a top manager is often named as a “pseudo-UBO” just to satisfy the rules.
- UBO Structure Chart: This is a visual map or diagram. It shows the layers of ownership from the local company all the way up to the human owners at the top.
- Ownership Threshold: This is the “trigger” percentage. In the Netherlands and the EU, if you own 25% or more, you are usually considered a UBO. In some high-risk cases, this drops to 10%.
- Compliance Chain: Think of this as a domino effect. A bank asks a company for UBO data; that company then has to ask its suppliers, who then have to ask their manufacturers. This is why these clauses are suddenly appearing in almost every contract.
Understanding UBOs – What Is It Exactly and Why is it Important?
An Ultimate Beneficial Owner is the natural person who ultimately owns or controls a legal entity. This can even be the case if their name doesn’t appear directly on ownership documents. Typically, this includes individuals who own more than 25% of shares or voting rights. Sometimes, this threshold may be as low as 10% in some contexts. It also encompasses those who exercise control through other means, such as appointment rights or veto powers. When ownership is widely distributed with no individual meeting these criteria, a senior managing official may be designated as a “pseudo-UBO” for compliance purposes.
The importance of UBO requirements in business relationships originates from what can be described as a compliance chain. Initially confined to financial institutions under anti-money laundering regulations, these requirements now cascade through various industries. For example, a payment processor might require UBO information from an e-commerce company. This company will in turn requests this information from its suppliers. Finally, these suppliers then include UBO disclosure requirements in their contracts with manufacturers. This chain reaction explains why UBO clauses increasingly appear in contracts across sectors that previously had minimal regulatory oversight.
Legal Framework: Global, EU, and Dutch Requirements
Before we go into the key industries & contracts involved, let us start at he beginning. What is the legal framework where these burdensome UBO’s originate from? Many countries and global organizations have implemented measures to combat money laundering and terrorist financing. As countries have diverse legal, administrative and operational frameworks and different financial systems, measures to counter these threats differ greatly per country and region.
Global UBO Standards
Globally, most countries have developed UBO standards in response to international initiatives against money laundering and financial crime. While approaches vary by jurisdiction, several organizations, initiatives and common principles have emerged:
- FATF Recommendations (see link): Recommendations (24 and 25) that require countries to ensure transparency regarding beneficial ownership of legal entities
- Varying Implementation: Globally, most countries have established beneficial ownership registries with different thresholds and accessibility levels.
- Accelerated Transparency: The Panama Papers and Paradise Papers revelations exposed how anonymous structures facilitate financial crimes
- Information Sharing: The OECD’s Common Reporting Standard (see link) enables automatic exchange of financial account information between tax authorities
- Compliance Complexity: Multinational companies face a patchwork of requirements necessitating country-specific approaches
European Union Regulatory Framework
The EU has established one of the world’s most comprehensive UBO disclosure regimes, especially under the Anti-Money Laundering Directives (AMLD):
- AMLD: The 4th AMLD required central UBO registries, the 5th mandated public access, and the 6th strengthened enforcement.
- Ownership Definition: A beneficial owner is any natural person who owns or controls at least 25% of shares/voting rights or exercises control via other means.
- Public Accessibility: The 5th AMLD mandated public access to beneficial ownership information for companies and commercial trusts. Due to an EU court ruling, several EU member states, including Luxembourg and the Netherlands, moved to restrict public access to their beneficial ownership registers until legislative adjustments are made.
- Criminal Penalties: The 6th AMLD enhanced criminal penalties for money laundering offenses and expanded corporate criminal liability.
- National Variations: Despite the common framework, implementation varies between member states, creating compliance challenges for cross-border businesses.
The Netherlands: Specific UBO Requirements
The Netherlands implemented the EU’s UBO requirements with specific national provisions:
- UBO Registration Act: Dutch entities are required to register UBOs in the Dutch Commercial Register (Kamer van Koophandel) (since Sept. 2020)
- Public Information or restricted? It was the intention that the information would be public. Due to privacy (and security) concerns, restrictions were set up as to the public availability. See more on this subject from the Dutch government on this subject here: link.
- Verification Duty: Entities must take “reasonable measures” to identify and verify UBOs, maintaining internal records.
- Penalties: Administrative sanctions include fines up to €21,750, with criminal sanctions for intentional violations.
- Updating Requirement: Companies must update UBO information within seven days of becoming aware of any changes.
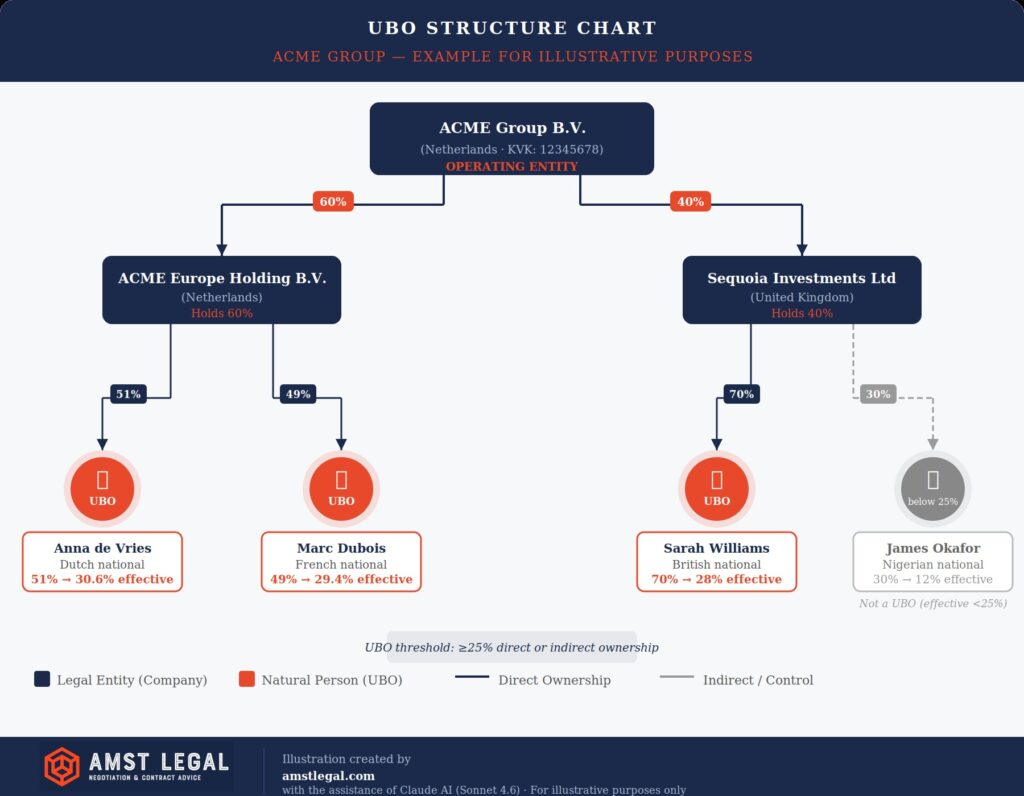
The Practical Value of a ‘UBO Structure Chart‘
We see many professionals searching for a “UBO structure chart”. Trying to explain a complex web of holding companies in an email is difficult for auditors to follow. A clear visual chart is the most effective way to provide this information and keep a deal moving.
Using Visuals to Speed Up Deals
In my work as an interim GC for various SaaS & Tech companies, we use these charts to simplify things for procurement, sales and finance teams. If you send a 20-page legal memo, it’s going to sit in someone’s inbox for a week. If you send a one-page UBO structure chart, you can often cut onboarding time by 40%.
At companies like twelve.eu or Construsoft, where things move fast, having this chart ready to go means the “KYC” (Know Your Customer) process won’t kill your deal momentum. Also see our article here how we suggest to improve KYC processes in your company.
Key Industries and Contracts Where UBO Matters
The importance of UBO disclosure varies significantly across industries and contract types. While requirements can appear in almost any business relationship, six industries face particularly frequent and stringent UBO disclosure requirements:
List of Industries
- Financial Services: Banks, payment processors, investment firms, and insurance companies face the most comprehensive regulatory mandates
- Real Estate: Commercial property transactions, development projects, and property management services
- Technology: Software providers, cloud services, and cybersecurity companies, especially those handling sensitive data
- Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals: Medical device manufacturers, pharmaceutical distributors, and healthcare service providers
- Government Contractors: Companies in defense, infrastructure, public utilities, and other sectors serving government entities
- Professional Services: Law firms, accounting practices, consulting firms, and other advisors with fiduciary responsibilities
Financial services companies naturally face the most stringent requirements, with banks, payment processors, investment firms, and insurance companies all subject to explicit regulatory mandates. However, several other sectors now routinely encounter UBO requirements in their operations.
Real estate transactions frequently involve UBO disclosure, particularly for commercial property acquisitions and development projects. A commercial real estate firm recently had to delay closing on a major property acquisition because their ownership structure involved multiple layers of holding companies, and the lender required complete UBO transparency before approving financing. Companies in this sector should prepare UBO documentation well before entering into purchase agreements or seeking financing.
Technology companies, particularly those handling sensitive data or providing critical infrastructure services, increasingly face UBO scrutiny. Government contracts almost universally require UBO disclosure, and many enterprise clients now include these requirements in their vendor security assessments. A cybersecurity provider lost a promising government contract because they couldn’t adequately document the beneficial ownership of one of their offshore investment partners within the required timeframe.
In healthcare and pharmaceuticals, UBO requirements appear in various contexts, from hospital system vendor agreements to pharmaceutical distribution contracts. Regulatory concerns about conflicts of interest and the integrity of the healthcare supply chain have intensified focus on ownership transparency. A medical device manufacturer was surprised when a hospital system required UBO disclosure before finalizing a procurement agreement, a requirement that stemmed from the hospital’s compliance policies rather than direct regulatory mandates.
Types of Contracts involved
The types of contracts where UBO disclosure commonly appears include:
- Financial agreements (loans, investment documents, banking relationships)
- Government and public sector contracts at all levels
- Long-term supply or service agreements, particularly in regulated industries
- Joint venture and partnership agreements
- Property purchase and lease agreements for commercial real estate
- Merger and acquisition documentation
- Distribution agreements, especially cross-border arrangements
- Software and technology licensing for enterprise solutions
A manufacturing company was caught off-guard when their standard distribution agreement with a European partner suddenly included UBO requirements, delaying their expansion plans by several months. Had they anticipated this increasingly common contractual element, they could have prepared the necessary documentation in advance rather than scrambling to compile it under time pressure.
Managing UBO Requests: The Dual Challenge
Requesting UBO Information Effectively
Many businesses find themselves needing to request UBO information from counterparties. Even a software company we recently advised includes UBO disclosure requirements in their enterprise contracts because their payment processor requires them to identify the UBOs of clients generating significant annual revenue. While the clause appears in their standard contracts, they actively enforce it only for larger clients, creating a tiered approach that balances compliance with practical business considerations.
When requesting UBO information, clarity is crucial. Rather than simply demanding “beneficial ownership information,” specify the ownership threshold that triggers disclosure, the documentation required for verification, how ownership changes should be reported, and the consequences of providing false information. A manufacturing client improved their compliance process by creating a detailed UBO information request form that clearly outlined these requirements, reducing back-and-forth communications and accelerating their onboarding process by nearly 40%.
Providing UBO Information Efficiently
Most businesses will also find themselves needing to provide UBO information to partners, financial institutions, or customers. A technology services provider we work with recently secured a major contract partly because they could provide comprehensive UBO information within 24 hours, while competitors took days or weeks. The client, under pressure to implement a new system quickly, viewed this efficiency as a demonstration of operational excellence and organizational reliability.
The key to responding quickly to UBO requests lies in preparation. Companies that maintain current UBO documentation and have streamlined processes for responding to requests gain a distinct advantage. A distribution company that previously scrambled to gather UBO information when requested implemented a quarterly review process that ensures their documentation remains current, reducing their response time from weeks to hours and eliminating the frantic search for information that previously disrupted operations.
Building an Effective UBO Management Framework
Implementing a structured approach to UBO management can transform a potential compliance headache into a streamlined process. Consider these five essential elements that successful companies have implemented:
- Centralized ownership intelligence: Maintain a single source of truth for all ownership information, including complex group structures. A multinational technology company created significant efficiencies by consolidating ownership data previously scattered across legal entities into a single database accessible to authorized employees.
- Proactive disclosure templates: Develop standardized formats for different disclosure requirements. A software company we advised created three different UBO disclosure templates—basic (10% threshold), standard (25% threshold), and comprehensive (includes indirect control)—allowing them to quickly respond to requests with varying requirements.
- Clear escalation pathways: Establish procedures for handling complex or unusual UBO requests. We helped a retail chain that implemented a tiered approach. Routine requests are handled by their dedicated back office & paralegal team handling UBO requests, while requests involving sensitive jurisdictions or unusual thresholds are escalated to the legal manager and/or senior management.
- Compliance calendar: Create a schedule of required reviews and updates based on both internal policies and external requirements. A financial services firm avoided penalties by implementing quarterly ownership reviews synchronized with regulatory reporting deadlines.
- Documentation hierarchy: Establish a clear hierarchy of documentation, from primary sources (share registers, articles of incorporation) to derivative summaries. A Bio-Tech client streamlined their process by maintaining both detailed supporting documentation and executive summaries tailored to different audiences.
Comprehensive Documentation Management
The foundation of effective UBO management is comprehensive, standardized documentation. An international consulting firm created what they call a “UBO passport” – a standardized digital package containing all essential UBO information in formats that satisfy various requesting entities. This package includes a visual representation of their ownership structure, standardized declaration forms for all UBOs, verified identification documents, and supporting evidence of ownership claims.
The firm reviews and updates this package quarterly, ensuring they’re always prepared to respond to UBO requests. When a potential client recently requested UBO information as part of their vendor onboarding process, the firm provided their complete package within hours, impressing the client with their professionalism and accelerating the contract negotiation process.
Establishing Clear Communication Protocols
UBO requests often create urgency because they involve sensitive personal information and complex corporate structures. A real estate development group created an internal UBO communication protocol that specifies exactly who should be contacted when UBO information is required, what information can be shared with whom, and how sensitive documents should be transmitted.
Their protocol includes a designated email address for all UBO-related communications, templates for requesting additional information from shareholders, and secure file-sharing procedures for transmitting sensitive documents. When a banking partner recently requested updated UBO information with a tight deadline, this clear protocol enabled them to gather and provide the necessary information without the confusion and delays that had previously hampered similar requests.
Assigning Dedicated Responsibility
UBO compliance requires dedicated responsibility and clear accountability. A manufacturing client previously experienced significant delays in contract negotiations because their UBO information was scattered across different departments with no clear ownership. By designating their corporate counsel as the “UBO officer” with authority to maintain and provide this information, they reduced their response time from weeks to days.
In smaller organizations, this responsibility might fall to the CFO or general counsel, while larger entities might have a dedicated compliance function. Regardless of company size, having at least one backup person familiar with UBO processes ensures continuity during absences. A technology company implemented this approach after losing a potential partnership when the only person familiar with their UBO documentation was unavailable during a critical negotiation period.
Implementing Regular Review Processes
UBO information isn’t static – ownership structures change, controlling interests evolve, and regulatory requirements update. A financial services firm implemented a monthly UBO review process after experiencing a significant compliance issue when a major shareholder’s reorganization wasn’t properly reflected in their UBO documentation. This proactive approach has prevented similar issues and demonstrated their commitment to regulatory compliance to partners and regulators alike.
When you set up an Effective review processes, include scheduled periodic reviews (even when no changes are known). These reviews ensure that, whenever there’s a shift in ownership or control, the necessary reporting is up to date. A healthcare technology company avoided potential regulatory penalties by identifying a previously undisclosed beneficial owner during one of their quarterly reviews, allowing them to update their regulatory filings before an upcoming audit.
Leveraging Appropriate Technology
For companies with complex ownership structures or frequent UBO requests, technology can significantly enhance efficiency. An international retail group implemented a dedicated UBO management module in their compliance system that allows them to track UBO information, set automated review reminders, and quickly generate reports in various formats requested by different partners and regulators.
Technology solutions might include centralized document management systems with appropriate access controls, automated verification tools that check UBO information against public records, workflow tools to track requests and approvals, and calendar systems for review reminders. Even smaller companies can benefit from relatively simple technological approaches. For example: encrypted storage systems for sensitive documents and standardized digital templates for UBO information.
From Compliance Burden to Strategic Advantage
Companies that excel at UBO management transform what many view as a regulatory burden into a strategic advantage. A private equity firm noted that they give preferential consideration to investment opportunities where the company can quickly provide accurate UBO information. To them, it indicates not only regulatory compliance but also good governance and organizational discipline – qualities that significantly impact investment decisions.
Speed in providing UBO information can be particularly valuable in time-sensitive transactions. A technology services provider recently won a significant contract partly because they could provide comprehensive UBO information immediately, while their competitors required days to gather the same information. The client, facing tight implementation deadlines, viewed this efficiency as a positive indicator of the provider’s overall operational excellence.
Beyond speed, transparency in UBO matters builds trust with partners, clients, and regulators. A pharmaceutical distribution company that had previously been hesitant to disclose ownership information found that their new proactive approach to UBO transparency actually opened doors to partnerships with larger organizations that valued their clear governance structures and compliance mindset.
Privacy Concerns: Does AI Store Your UBO Data?
A common question lately is: “Does Claude train on my data?“. What if I add my UBO information in Claude, is this public? As we use more digital tools to manage compliance, understanding where your data goes is essential. See our article ‘Anthropic’s Claude AI Updates – Impact on Privacy & Confidentiality’ here.
Managing Sensitive Ownership Info
As a founder who handles legal and interim work, I understand why people are nervous about putting ownership data into AI tools. That is the reason we wrote the article referred to above and the article ‘Ultimate Guide how ChatGPT, Perplexity and Claude use Your Data’ here.
Important to remember is this: Why “Pro” Doesn’t Mean Professional: Claude Pro costs $20 monthly but remains a consumer account. The name suggests business-grade protection, but that is not correct. Similarly, Team accounts at $30 monthly sound enterprise-ready. They’re actually consumer tier with training enabled by default. Main lesson: if you are not using a business account (remember that Pro is not a business account) disable training on your data here.
- Confidentiality: Professional AI versions (like Claude or Gemini on a paid Team or Enterprise plan) generally have strict rules against using your uploads to train their models. Check each AI model or AI company where you include this information. If necessary, disable training on your data for each AI model.
- Best Practice: Only use AI for UBO work if you are on a Team or Enterprise plan with a solid Service Level Agreement (SLA). As always, If not enabled by default, disable training on your data for each AI model.
- The Smart Move: Keep your primary, sensitive documents in your secure vault. Use the AI only to help write the summaries or descriptions you need for the structure chart.
To ensure your article on amstlegal.com is fully optimized for both search engines and executive readers, here is the final FAQ section with five strategic points. This section is designed to capture high-intent search queries like “UBO meaning” and “UBO full form” while addressing the modern privacy concerns you’re seeing in your search data.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on UBO Compliance
1. What is the UBO full form and its core meaning?
The UBO full form is Ultimate Beneficial Owner. The UBO meaning refers to the specific natural person who ultimately owns or controls a legal entity. Even if a company is owned by several other holding companies, the UBO is the human being at the very top of that chain.
2. What is the standard ownership threshold for a UBO?
In the Netherlands and throughout the EU, the standard threshold is 25% or more of shares, voting rights, or ownership interest. However, in certain high-risk sectors or complex structures, banks and regulators may lower this “trigger” to 10% to ensure full transparency.
3. Why is a UBO structure chart necessary for my business?
A UBO structure chart is a visual map that satisfies the “Verification Duty” of banks and partners. Instead of providing a stack of legal documents, a clear chart explains complex holding layers at a glance. At AMST Legal, we’ve seen these charts reduce onboarding time by 40% for companies working with partners like Booking.com or PVH.
4. Who is considered a “pseudo-UBO”?
If no natural person owns more than 25% of a company—common in large, widely-held corporations—you must still designate a UBO. In these cases, a senior managing official (such as a CEO or Managing Director) is registered as a pseudo-UBO to ensure there is always a human point of accountability.
5. Is it safe to use AI tools like Claude to manage my UBO data?
This is a frequent concern for modern legal teams. While tools like Claude (especially on Team or Enterprise plans) offer significant data privacy protections, you should never upload unredacted, highly sensitive documents without a formal Service Level Agreement (SLA). The best approach is to keep primary documents in a secure vault and use AI only to help summarize or describe the structures for your UBO structure chart.
Conclusion
Structured Approach
UBO requirements have become a standard feature of the business landscape. Rather than treating these requirements as a burden or an afterthought, forward-thinking companies implement structured approaches that turn UBO compliance into a business advantage. By developing comprehensive documentation, establishing clear communication protocols, assigning dedicated responsibility, implementing regular review processes, and leveraging appropriate technology, organizations can transform UBO compliance from a source of delay into a demonstration of operational excellence.
Proactive Approach
Whether you’re requesting UBO information from others or providing it in response to contractual requirements, a proactive approach will save time, reduce risk, build trust, and potentially give you an edge in competitive situations. In today’s complex regulatory environment, effective UBO management isn’t just about compliance – it’s about strategic business advantage.
About AMST Legal
At AMST Legal, we provide advice how to improve your (legal) processes. Compliance work – like UBO requests – is part of that. Contact us at info@amstlegal.com or book a meeting here for help with your legal (compliance) framework.

30 of the Best Questions to Ask in Any Negotiation
Asking the right questions is one of the most important parts of any successful negotiation – next to preparation. Great questions drive the conversation, uncover needs and reveal hidden interests. The quality of your negotiation questions determines the quality of the information you gather, the solutions you co-create, and ultimately, the agreements you reach. This is why we wrote this article ’40 of the Best Questions to Ask in Any Negotiation’. See below our explanation of how great questions are set up and our list of the best questions you can use in any negotiation.
Think about it, when you are communicating, there is so much hidden value that you are able to unlock with your questions.
In this article we dive into the most effective questions to ask in any negotiation and frankly in any interaction. I like to refer to these questions as High Quality Questions. We will first focus on best practices for Asking Great Questions and list “How” “What” and “Why” questions, as well as essential phrases that every negotiator should have in their toolkit. This will guide you through discussions, resolve disagreements and reach meaningful outcomes.
Executive Summary: The TLDR of Strategic Inquiry
The Bottom Line: Negotiation is an information game. To de-risk contracts and unlock commercial value, shift from “persuading” to “inquiring.”
- The Framework: High-Quality Questions (open-ended “How” and “What”) move counterparts from rigid positions to underlying interests.
- W.A.I.S.T. & Strategic Silence: Ask the question, then stop talking. Silence is where the most valuable “hidden truths” are revealed.
- Land the Plane: Concise inquiry projects confidence. Avoid over-explaining your questions; let the other party fill the gap.
- Discovery over Defense: If you aren’t listening for the intent behind the words, you are missing the deal.
The ROI of Inquiry in Negotiations: Why Strategic Questions Win Deals
Before diving into the specific toolkit, we must understand the commercial impact and the foundational terms that drive successful outcomes. At AMST Legal, we don’t just provide “tips”; we provide a framework for Negotiation Inquiry and High-Quality Questions (HQQs). For our international partners and those new to the field, these terms are the cornerstones of a sophisticated deal-making strategy.
Defining Negotiation and Strategic Inquiry
To ensure all stakeholders—from Legal to Sales—are aligned, we define these core concepts:
- High-Quality Question (HQQ): A strategic, open-ended inquiry designed to pivot a negotiation from rigid, adversarial positions toward shared underlying interests and bilateral value creation.
- Negotiation: A back-and-forth communication process aimed at reaching an agreement when you and the other party have some shared interests and some that are opposed. It is a collaborative exercise in problem-solving where the goal is a sustainable, binding commitment.
- Negotiation Inquiry: The intentional and systematic use of questions to gather intelligence, test assumptions, and shift the focus from what someone is asking for (their position) to why they are asking for it (their interest).
The Power of Asking the Right Questions
In my work as a Legal Counsel for Booking.com, Tommy Hilfiger and Calvin Klein, I noticed that the person asking the questions is the one actually in control of the room. Expert negotiators at companies like Booking.com, Servicenow.com and PVH focus on their Negotiation Inquiry strategy to control the flow and risk of a deal.
HQQs act as a diagnostic tool rather than just a communication method. For example, instead of arguing over a liability cap for three hours, a single question (e.g.“What is the specific catastrophic scenario your board is most concerned about?”) can bypass weeks of legal friction. By using high-quality inquiry, you aren’t just “talking”; you are performing a risk-assessment in real-time. This shifts the dynamic from a battle of wills to a shared search for solutions. Asking the right negotiation questions can truly change any conversation. Also see our article ‘7 Tips How to Improve Live Contract Negotiations’ here.
What We Will Cover
In this article, we explore the mechanics of high-stakes inquiry. You will learn:
- The 4 Core Principles: From “Landing the Plane” to “Strategic Silence.”
- The HQQ Toolkit: A categorized list of 30 “How,” “What,” and “Why” questions designed for sales, procurement, and legal teams.
- Practical Discovery: Phrases and active listening strategies used by elite negotiators.
- The FAQ of Inquiry: Quick answers to the most common negotiation roadblocks.
Four Core Principles for Asking Great Questions
Before diving into the specific types of questions you should use in negotiations, it’s important to pause and understand why the quality matters so much. Asking great questions is not just about curiosity – it’s about strategy. High-quality questions are tools that unlock insights, foster collaboration, and lead the way for creative solutions.
Many negotiations fail not because of a lack of preparation but because one side fails to ask the right questions or listens poorly to the answers. By mastering the way you ask questions, you show confidence, demonstrate that you value the other person’s perspective, and gain access to critical information that can tip the scales in your favor.
However, asking effective questions requires discipline. It’s not just about what you ask but how you ask. Before we go into the best questions to ask, we will list the four key principles to keep in mind.
1. Ask Open Questions – Avoid ‘Yes’ or ‘No’ Questions
Open-ended questions are one of the most powerful tools in a negotiator’s toolkit. Questions that can be answered with a simple “yes” or “no” tend to shut down conversations rather than open them up. For example:
- Instead of asking, “Do you agree with this price?” or “Did you have a nice holiday” etc
- Try, “What are your thoughts on this pricing?” or “Tell Me About Your Holiday“.
The second approach encourages the other party to elaborate, giving you valuable insights into their reasoning, concerns, or hesitations. Open-ended questions invite dialogue, uncover motivations, and often reveal opportunities to find common ground.
When you ask open-ended questions, you position yourself as someone genuinely interested in understanding the other side, which builds trust – a crucial element of any negotiation.
See this great article “Asking Open-Ended Questions Increases Personal Gains in Negotiations” from Matteo Di Stasi, Alison Wood Brooks, and Jordi Quoidbach on this subject.
2. W.A.I.(S.)T. – Why Am I (Still) Talking?
What does the principle of WAIST mean? It is a simple yet often overlooked: ask your question, then stop talking. Silence may feel uncomfortable, but it’s one of the most effective tools a negotiator can use. Many people sabotage their own questions by filling the silence with explanations or, worse, answering the question themselves.
WAIST can be used in any situation where you have been talking too long. Anything you are speaking longer than 3-4 sentences, especially in negotiations, stop and ask a HQQ question.
For example:
- Asking, “How does this align with your goals?” is a great question. However, if you then immediately add for example, “I mean, I assume it does not fully align, but we can discuss…?” undermines the power of the question.
- During contract negotiations you might ask: “Does this new wording in Art X work for you?” and then immediately filling the silence with assumptions like, “I assume it’s probably not fully aligned with your proposed wording, but I am sure we can work something out….” would again not be advised. Ask your question and wait for your answer. Wait and allow the other side to respond. Their answer might surprise you, such as: “Actually, the wording is fine, except for this one word. Would this alternative work for you?”
By thinking about the concept “W.A.I.S.T. – Why Am I Still Talking?” – you give the other party space to think, process, and provide a meaningful answer. The silence you leave can be a powerful motivator for the other person to fill it with their thoughts, which often reveals more than you might expect. Insight: by staying quiet, you avoid creating problems that don’t exist and let the real issue surface.
3. Land the Plane
The concept of “W.A.I.S.T.” and “Land the Plane” comes from Alexandra Carter’s book, “Ask For More – 10 Questions to Ask to Get What You Want. It’s about asking a clear, concise question and then stopping – giving the other party space to respond. Many negotiators undermine their own questions by “circling the runway,” over-explaining, or talking too much.
Next time you are negotiating or just talking to someone. observe if this happens. You will notice that many people ask a question but complete it themselves without waiting for the answer.
For example:
- Instead of asking, “How does this price fit within your budget?” and then nervously adding, “I mean, if it doesn’t work, we can look at discounts, or we can split it into payments…”
- Simply ask: “How does this price fit within your budget?”
Why does this work?
When you “land the plane,” you:
- Avoid diluting your message. Adding extra words or unnecessary suggestions often weakens the strength of your question.
- Give the other party room to think and answer. Negotiations require processing time. Silence often encourages deeper responses.
- Project confidence. A clear question followed by quiet shows that you value their input and are comfortable waiting.
4. Active Listening
Active listening is a very powerful tool that I learned from the Harvard Program on Negotiation, but a lot has been written about the subject. s not just about hearing words – it’s about understanding, processing, and responding thoughtfully. Effective negotiators don’t just wait for their turn to speak; they listen carefully and build their follow-up questions based on what was said.
What Is Active Listening?
As mentioned in a recent Harvard Business Review article, active listening is when you not only hear what someone is saying, but also attune to their thoughts and feelings. It turns a conversation into an active, non-competitive, two-way interaction. Robin Abrahams and Boris Groysberg from Harvard Business School describe active listening as having three aspects: cognitive, emotional, and behavioral. Here’s how they define each aspect in their article, “How to Become a Better Listener”:
- Cognitive: Paying attention to all the information, both explicit and implicit, that you are receiving from the other person, comprehending, and integrating that information
- Emotional: Staying calm and compassionate during the conversation, including managing any emotional reactions (annoyance, boredom) you might experience
- Behavioral: Conveying interest and comprehension verbally and nonverbally
For example
- If the other party says, “We’re concerned about the delivery timeline,” an active listener might follow up with, “What part of the timeline feels unrealistic to you?”
- When your counterpart mentions: “We are particularly concerned about your liability clauses so we will need to go with our standards”, instead of going into a discussion why you should your standards (or not), ask what part of the clause they are concerned about and what the reason is of the concern.
This approach achieves two things:
- It shows the other party that you are engaged and care about their perspective.
- It gives you the chance to gather more information and address their concerns directly.
Active listening also helps avoid assumptions, which are a common pitfall in negotiations. When you listen deeply and ask relevant follow-up questions, you reduce the risk of misunderstanding and strengthen the quality of the dialogue.
Why These Rules Matter
The reason we reiterate these rules is that asking great questions is both an art and a skill. It requires intentionality, focus, and practice. When you master the art of asking clear, open-ended questions and combine it with active listening, you gain a huge advantage in any negotiation.
Think of it this way: questions are like keys. Some questions unlock doors to hidden opportunities, while others keep those doors firmly shut. By avoiding closed questions, staying silent after you ask, being concise, and actively listening, you ensure that you’re asking the right questions in the right way.
These rules serve as the foundation for all the “How,” “What,” and “Why” questions we’ll explore in this article. Use them consistently, and you’ll find that your conversations become more insightful, your relationships stronger, and your outcomes more favorable.
In short: ask well, listen better, and negotiate smarter.
30 Questions to Improve Your Negotiations
While we have specifically geared this list toward complex commercial negotiations, these questions are high-impact tools for any high-stakes interaction. Whether you are navigating a difficult conversation with family, aligning with internal stakeholders at work, or standing out in a job interview, the ability to ask a High-Quality Question (HQQ) is a universal superpower.
In a job interview, for instance, replacing a standard query with a strategic inquiry like, “What does success look like for this role in the first six months?” immediately signals that you are focused on value creation rather than just a paycheck. You can therefore also see this as the best questions to ask in an interview.
Let us now dive into the 30 best questions to ask, categorized by their strategic intent to help you control the room and uncover the hidden deal.
1. “HOW” Questions
“How” questions are powerful because they focus on process, possibility, and solutions. They encourage the other party to think constructively and collaboratively, which can shift negotiations from conflict to cooperation.
As Chris Voss explains in Never Split the Difference, “How” questions work particularly well because they force the other party to engage with your perspective without feeling attacked. For example, asking “How am I supposed to do that?” puts the burden of providing solutions back onto the other party.
Examples of “HOW” Questions
- How am I supposed to [do that/pay this]?
- How does this violate our agreement?
- How do we know?
- How can I help make this better for us?
- How on board are the people who are not here today?
- How would you feel if…?
Further Reading:
- How to Use “How” Questions in Negotiations – YouTube explanation from Chris Voss – The Black Swan Group (Book: Never Split the Difference).
- Getting to Yes: The Art of Collaborative Negotiation – Harvard PON.
2. “WHAT” Questions
“What” questions are neutral, open-ended, and non-confrontational. They work because they invite the other party to explain themselves without feeling defensive. According to negotiation theory from Getting to Yes, “What” questions help you uncover key interests and concerns.
For example:
- “What challenges do you see with this proposal?” encourages the other party to express their concerns openly, allowing you to address them proactively.
- “What is your biggest concern?” cuts through surface-level objections and gets to the root of the problem.
“What” questions also create opportunities for exploration and creativity, two elements that experts agree are critical in creating value during negotiations.
More Examples of “WHAT” Questions
- What else would you like us to know?
- What is the reason…?
- What if we tried…?
- What are your views on…?
- What challenges do you see with…?
- What is your biggest concern?
- What brought us into this situation?
Further Reading:
- Getting to Yes: The Power of Questions – Harvard Program on Negotiation.
- How to Ask Powerful Questions in Negotiation – Harvard Business Review.
3. “WHY” Questions
“Why” questions are excellent for uncovering motivations, values, and hidden interests, but they must be used carefully. While they can dig deeper into someone’s reasoning, poorly phrased “Why” questions may come across as accusatory or confrontational.
The key to using “Why” questions effectively, as emphasized in negotiation literature, is tone and intent. According to Fisher and Ury in Getting to Yes, asking “Why is this important to you?” encourages the other party to share their underlying interests without feeling attacked.
Additionally, “Why” questions help you test assumptions and challenge objections diplomatically. For example, “Why would this solution not work for you?” invites constructive feedback instead of resistance.
As mentioned by Chris Voss, you should avoid asking too many “Why” questions and use other high quality questions as ‘Why’ questions could have a negative connotation.
Examples of “WHY” Questions
- Why is this so important for you?
- Why is this unacceptable to you?
- Why should we consider…?
- Why should we delay an answer on this?
- Why would this solution not work for you?
- Why is this part of the article crucial for you?
Further Reading:
- See this video “The Secret Way To Use “Why” & “No” in Your Next Negotiation | Chris Voss”.
- The Psychology of ‘Why’ Questions in Negotiation – Psychology Today.
4. Great Phrases You Can Use
Also part of asking high quality questions is using effective phrases that create an atmosphere of collaboration and understanding. These phrases are excellent for encouraging dialogue, clarifying positions, and keeping the negotiation constructive.
It is advised to switch from How, Why and What questions to these kind of great phrases. The reason for this is that otherwise you questions might come across as an interrogation. This is also why the WAIST and Land the Plane principle is so important. Especially if you mix it up with Active Listening.
Examples of Great Phrases
- Is there anything I am missing…?
- Have you given up on this…?
- Is it okay if…?
- I am curious…
- It sounds like…
- Tell me about…
- OK, help me understand…
These phrases demonstrate humility, curiosity, and a desire to understand, which are key elements of building trust and achieving better results.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Negotiation Inquiry
Q: What is the most important question in any negotiation?
There isn’t one “magic” phrase, but the most effective questions are always open-ended. Focus on “How” and “What” to gather intelligence, and “Why” to uncover motivations.
Q: How do you handle a negotiator who gives one-word answers?
Use a “labeling” phrase like, “It sounds like there’s a piece of information you aren’t comfortable sharing yet,” and then rely on Strategic Silence. Let the discomfort of the pause do the work for you.
Q: Why should I avoid “Yes/No” questions?
Closed questions shut down the flow of information. Open questions encourage your counterpart to reveal their interests, which is the only way to create value in a complex contract.
Q: How do I ask for a concession without sounding aggressive?
Instead of demanding a change, frame it as a collaborative problem. Use a question like: “What would need to happen for us to find a middle ground on this specific delivery timeline?” This invites the other party to help solve your constraint rather than defending their position.
Conclusion
Asking high-quality questions is a game-changer in negotiations. By focusing on “How,” “What,” and “Why” questions, and complementing them with great phrases, you can steer conversations toward productive outcomes. Whether you’re addressing objections, seeking clarification or exploring solutions, it allows you to gain insights, uncover motivations, and move closer to a successful agreement. Read more here about where we could help you in your negotiations.
Also see the importance of great questions in this article ‘The Surprising Power of Questions’..
About AMST Legal
At AMST Legal, we provide negotiation and contract advice to help businesses achieve better results. Contact us at info@amstlegal.com or book a meeting here for help with a negotiation or for (team or individual) training to become a better negotiator.
DeepSeek – Is your Data Safe? Everything You Need to Know
In my previous article we examined how ChatGPT, Perplexity and Claude uses your data (AI data use). We also mentioned the potential risks of sharing confidential or proprietary information – and how to avoid these risks. It is clear that not all tools offer the same safeguards regarding data privacy, security, and legal protections. We will therefore continue comparing AI models. This week a focus on the AI model DeepSeek. See below our Article ‘DeepSeek – Is your Data Safe? Everything You Need to Know’.
DeepSeek was unknown to most people outside of the People’s Republic of China (“PRC“) until this week. In the course of one week it has however gained immensely in popularity. It is yet another AI-driven platform, but there are important differences with the other well-known AI models. DeepSeek is currently challenging AI models like ChatGPT and Gemini in capabilities unexpected until yesterday. In this article, we will explore DeepSeek’s Privacy Policy & Terms of Use. We will also handle issues such as personal data storage, AI model training and jurisdiction. If you’re wondering whether you can safely use DeepSeek for personal or professional tasks, read on to discover the key facts, risks and best practices.
This article has been written at the start of the broad use of DeepSeek. It is therefore work in progress, based on first information gathered.
What We’ll Cover
- DeepSeek Overview: Short explanation of the platform and why are people interested in it.
- Privacy Policy Highlights: Including details on storing personal data, especially full names and addresses.
- Location of Data: How and why user data may end up on servers in the People’s Republic of China.
- Terms of Use: Whether DeepSeek incorporates your content into training its AI models—and what that means for you.
- Data Privacy in China: The local regulatory environment and how it differs from GDPR or CCPA.
- Confidentiality: Potential risks if you’re handling sensitive or proprietary information.
- Final Advice: How to proceed if you’re considering using DeepSeek, plus some general cautionary steps.
1. DeepSeek Explained
New AI Model
DeepSeek is a cutting-edge large language model (LLM) similar to ChatGPT and Gemini. It is developed by a Chinese AI company with the full name ‘Hangzhou DeepSeek Artificial Intelligence Co., Ltd., and Beijing DeepSeek Artificial Intelligence Co., Ltd.’. It is designed to tackle a range of complex tasks with impressive efficiency according the latest tests. According to Google Gemini its powerful AI shines in several key areas:
- Math Whiz: DeepSeek excels at mathematical reasoning and problem-solving, often outperforming other models.
- Logic Master: DeepSeek handles complex, multi-step logical reasoning with ease.
- Code Conjurer: DeepSeek understands and generates code in various programming languages, making it a valuable tool for developers.
- Conversation Starter: DeepSeek is a natural language expert, capable of engaging in coherent and contextually relevant conversations.
- Global Communicator: DeepSeek is trained on diverse linguistic data, offering some level of multilingual support.
Consequences Stock Market
On 26 January 2025 there was even a big shake up in the stock market due to Deep Seek. US stocks plummeted as traders fled the tech sector and erased more than $1 trillion in market cap amid panic over the introduction of DeepSeek. The S&P 500 nearly 1.5% lower, while the tech-heavy Nasdaq Composite had shed more 3% by the end of the day. DeepSeek roiled stock futures after the AI model was said to outperform OpenAI’s ChatGPT in several tests. The losses gathered momentum after DeepSeek became the most downloaded app on Apple’s App Store in the US on 26 January.
Source: Business insider.
A Growing Global Market
As AI popularity expands worldwide, companies outside the U.S. and Europe (especially China) are developing their own solutions. DeepSeek is notable because it may offer high-speed performance and robust Chinese language capabilities. This makes it attractive to users with specialized language needs. However, these benefits come with a different legal framework, which can pose challenges for those used to Western data protection standards.
It has also been reported that DeepSeek is able to offer similar services and results as ChatGPT, Gemini, etc. for a fraction of the cost. This has greatly fueled popularity of the new AI model.
2. DeepSeek’s Privacy Policy: Personal Data Collection
Amongst others, according to a review of DeepSeek’s publicly accessible Privacy Policy, the platform collects a wide range of personal information. Qoute: “When you create an account, input content, contact us directly, or otherwise use the Services, you may provide some or all of the following information:
- Information When You Contact Us. When you contact us, we collect the information you send us, such as proof of identity or age, feedback or inquiries about your use of the Service or information about possible violations of our Terms of Service (our “Terms”) or other policies.
- Profile information. We collect information that you provide when you set up an account, such as your date of birth (where applicable), username, email address and/or telephone number, and password.
- User Input. When you use our Services, we may collect your text or audio input, prompt, uploaded files, feedback, chat history, or other content that you provide to our model and Services.
Additionally DeepSeek stores (i) Automatically Collected Information like technical information, usage information, cookies, payment information and (ii) information from other sources like login, signup or linked information.
Where Is Information Stored
DeepSeek explicitly states:
“The personal information we collect from you may be stored on a server located outside of the country where you live. We store the information we collect in secure servers located in the People’s Republic of China.
Where we transfer any personal information out of the country where you live, including for one or more of the purposes as set out in this Policy, we will do so in accordance with the requirements of applicable data protection laws.”
For many users – especially those in countries with stringent privacy regulations – this is significant. Your legal recourse to access, delete or restrict your data might be limited once it’s hosted on servers in the PRC.
How Is This Data Stored and Processed?
While the Privacy Policy mentions “secure servers,” it is not clear how they deal with specific practices such as:
- Encryption: Are your data and prompts encrypted at rest or in transit?
- Third-Party Sharing: How widely is your data shared for analytics or collaboration?
- Data Deletion: What happens if you decide to close your account or remove certain information?
- Data Security: How are the servers protected against e.g. cyberattacks.
If you’re accustomed to GDPR (EU Data Privacy Regulation) or CCPA (California Data Privacy Regulation), you may be disappointed by the lack of clearly defined user rights (like the right to be forgotten or the right to data portability). It remains to be seen how these matters are covered by DeepSeek. Especially from a regulatory point of view – data privacy, data security and now also AI (see the EU AI Act).
There are many more aspects that are very interesting in the DeepSeek Privacy Policy, but for the purposes of this article this would be too much information to touch on all aspects.
3. DeepSeek’s Terms of Use: Model Training & Governing Law
DeepSeek’s Terms of Use do mention that the AI model will only use your Inputs in specific cases. It is however not exactly clear how broad this should be read. See part below in blue. The terms also offer a way for its customers to inform DeepSeek that they refuse DeepSeek to allow to use their Input data.

Potential Risks for Confidential Information
When adding client documents, proprietary research, or any private data as always be mindful. As far as we are aware at this moment:
- No Guarantee of Confidentiality: There is no explicit promise to keep sensitive data confidential.
- Future AI Outputs: The model might inadvertently reveal or be influenced by your confidential info.
- Irreversible Submission: As DeepSeek’s Terms of Use do not mention how long DeepSeek will store your data, this will allow indefinite use of your data.
- Unclear use of Input: it is not exactly clear how and in which cases your Inputs will be used to create Outputs or to train the model. It is likely and we should assume that DeepSeek uses your Input to train their AI model.
Governing Law and Jurisdiction
Next, let’s review the terms regarding governing law and jurisdiction, meaning the laws that govern the use of DeepSeek and where you will need to go to court in case of litigation with DeepSeek. DeepSeek clarifies this as follows in the Terms of Use:
9. Governing Law and Jurisdiction
9.1 The establishment, execution, interpretation, and resolution of disputes under these Terms shall be governed by the laws of the People’s Republic of China in the mainland.
9.2 If negotiation fails in resolving disputes, either Party may file a lawsuit with a court having jurisdiction over the location of Hangzhou DeepSeek Artificial Intelligence Co., Ltd.
This means:
- The laws of the People’s Republic of China govern all legal disputes.
- Chinese courts in Hangzhou, PRC, will handle any lawsuits.
- Even though it is stated in the terms that DeepSeek will comply with applicable laws, research still needs to be done whether they will comply with GDPR, CCPA or other foreign regulations.
4. Data Privacy in China
In the EU and US there have been large initiatives since 2018 with respect to extensive legislation relating to the protection of data privacy and data security. In the coming years there will even be more regulations in connection hereto. See our article ‘Six New EU Regulations – like the AI Act – Explained‘.
Regulatory Differences
While China has its Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL), it doesn’t mirror the scope or depth of frameworks like GDPR or CCPA or the other regulations mentioned above – as far as we are aware but we are not lawyers or legal advisors versed in PRC laws.
Implications for International Users
If you reside outside China:
- Limited Recourse: You might find it harder to challenge data privacy & security issues in a Chinese court.
- Compliance Gaps: The data privacy and data security protections you are used to under EU or U.S. law may not apply here.
- Cross-Border Transfers: Even if the Privacy Policy mentions meeting local regulations, these could be PRC regulations that differ significantly from your home country’s standards.
5. Which Data Not to Share in AI Models
As we stated in our article with respect ChatGPT, Gemini and Perplexity, apply common sense and caution when adding data to any online AI model. This could be different for local models – depending on the security measures taken by the AI model.
Avoid sharing for example:
- Confidential details (client, business or family member names, private letters, contracts & strategies).
- Personally identifiable information (PII) (addresses, phone numbers, medical records).
- Proprietary or business-critical data (unreleased products, prices, financials).
- Sensitive materials (health info, internal memos, or business & personal).
- Data protected by Applicable Law (copyright, illegal data, government data).
If you must work with potentially sensitive text, we recommend considering the following:
- anonymizing the data first,
- using an enterprise-level AI solution where the Terms of Use prohibit using your content for model training. This doe not seem to be possible for DeepSeek, or
- an ‘on-premise’ AI model that anonymizes data.
6. Bringing It All Together
DeepSeek represents an interesting expansion of the AI landscape, especially for those who require strong Chinese language capabilities or want to explore AI solutions outside typical Western providers. However, its legal environment, data storage location, and governing jurisdiction all point to a platform that may not uphold the same privacy or confidentiality standards you’d expect under GDPR or CCPA.
This doesn’t mean DeepSeek is without merit. You should approach it with open eyes and informed caution. If you have critical confidentiality needs or work in a heavily regulated sector, it is wise to look elsewhere or secure a specialized enterprise agreement that explicitly addresses data protection concerns. For casual or non-sensitive uses, DeepSeek could be a helpful AI resource. As always, be mindful of what you submit and how it could be stored and potentially accessed under Chinese law.
7. Final Thoughts
AI is transforming the way we work – but it’s also transforming how data can move beyond our control. It is advised to think twice before you add content to any AI (LLM) Tool and actively keep track of how your content is used by any AI tool.
As always, we need to stay informed, be cautious and be proactive. That way, you can use the power of AI without compromising your most sensitive information. Keep an eye out for our upcoming in-depth articles on other AI models. We will also cover AI policies that can guide you and your team toward ethical and secure usage of these exciting new technologies.
Disclaimer: This article is a research project, provides general information about AI data usage and does not constitute legal advice.
If you have any further questions about the above, contact me via lowa@amstlegal.com or set up a meeting directly here .
To read more on this topic here is Ultimate Guide how ChatGPT, Perplexity and Claude use Your Data, Anthropic’s Claude AI Updates – Impact on Privacy & Confidentiality, South Korea spy agency says DeepSeek ‘excessively’ collects personal data, Berlin’s data protection commissioner reports the AI app DeepSeek to Apple and Google in Germany as containing illegal content, Is DeepSeek safe to use?

Automatic Price Increases in Contracts: What You Need to Know
Price increases – inflation

The Best Way to Efficient Contract Redlining in Negotiations
Lately, there has been a discussions about the best way to redline a contract during negotiations. When redlining a contract, should you simply send an amended redlined Word document and move on? Or should you adopt a more elaborate 6-step plan (including a pdf compare), as highlighted in various legal circles? When we talk about contract redlining, we mean ‘𝘵𝘩𝘦 𝘱𝘳𝘰𝘤𝘦𝘴𝘴 𝘰𝘧 𝘦𝘥𝘪𝘵𝘪𝘯𝘨 𝘢 𝘤𝘰𝘯𝘵𝘳𝘢𝘤𝘵 𝘸𝘩𝘦𝘯 𝘯𝘦𝘨𝘰𝘵𝘪𝘢𝘵𝘪𝘯𝘨’.
In this article ‘The Ultimate Guide to Efficient Contract Redlining in Negotiations’, you will find an in-depth look at how each contract redlining approach works.
I will also explain why we at AMST Legal believe continuing in one evolving redlined document (with occasional compares) is usually the most efficient, transparent and client-friendly method. We will also explore Nada Alnajafi’s (writer of the book Contract Redlining Etiquette) 10-step process so you can see precisely how an experienced contracts professional handles redlining from start to finish.
1. What We Will Cover
- Why the Debate? The origins of the 6-step approach vs. a single redlined doc
- Key Principles: Efficiency, transparency, and clarity for all parties
- When (and How) to Use Compares: Ensuring every edit is captured accurately
- When (and Why) to Avoid Extra PDFs: Why separate PDFs often add clutter
- Nada Alnajafi’s 10 Steps (Quoted in Full): A data-backed method for efficient redlining
- Final Takeaways: The balanced approach that works for most teams
2. Understanding the Debate
The Six-Step Approach vs. a Single Redline Document
As mentioned in my post on Linkedin on this subject, we noticed that in some legal circles, lawyers have embraced a 6-step process to handle contract edits. After they receive the new draft from the counterparty, they take the following steps:
- Accept all changes in the document you receive from the counterparty you are negotiating with (your new “clean” version).
- Compare old vs. this new draft to ensure that all changes compared to the previous version are visible.
- Amend the new “clean” version (can be amended by one or multiple people in the same organization).
- When finalized with adding comments & amendments, Compare again to show new changes to counterparty and to make the final check.
- Save the fresh comparison as a PDF.
- Send both the new “clean” doc (as amended) + the compare PDF.
For the avoidance of doubt, at AMST Legal we do not recommend this approach, except where agreed or desired by your client, customer or counterparty.
Advocates of this 6 step approach argue it helps manage large, complex deals – especially when multiple stakeholders are involved – by producing a neat record of only the latest changes.
Critics see it as time-consuming overkill that can inflate billable hours, make negotiations overly complicated and confuse counterparties who want to see comments and explanations in one place.
We have found that most:
- Critics are legal professionals involved in negotiating commercial contracts like NDA’s, MSA’s, sales, procurement and partner agreements.
- Advocates are lawyers in Big Law (large law firms) that are involved in finance and corporate transactions.
In general, most legal professionals seem to prefer to stick with one progressive redlined document, continuously layering edits and resolving comments as issues are settled. This single-document approach is often more efficient for commercial & smaller deals or simpler contracts, and it preserves the full negotiation trail.
Origins of the 6-Step Approach
The more traditional “clean + PDF compare” method likely emerged when Microsoft Word’s Track Changes was buggy or unreliable in large documents. Many practitioners still worry about hidden edits or formatting issues – concerns that, at one time, were quite valid. Others claim that by resetting to a “clean” version each time, you reduce the clutter of multiple layers of color-coded changes and make it simpler for executives to see only newly introduced edits.
However, Word has significantly improved in comparing documents and most commercial legal professionals do not believe that separate software like Litera and Deltaview) is still necessary. Additionally, best practices between legal professionals have been developed and are widely in use that mitigate most of these issues. That’s why many in-house counsel and lean legal teams opt to remain in a single track-changed doc for efficiency.
3. Key Principles of Effective Contract Redlining
Efficiency
As also advocated by Nada Alnajafi here, in a commercial setting, it’s typically best to redline a single version of the contract. Next to adding explanatory comments, you accept or reject changes as you reach agreement, and layer any new edits into the same tracked document.
This approach:
- Reduces confusion by keeping one “source of truth.”
- Retains comments in context, showing how and why each change evolved.
- Saves time for your counterparties, who don’t have to juggle multiple files.
Transparency
Continuous redlining gives all parties a full view of the agreement’s evolution. Rather than delivering a “clean” Word doc that erases prior edits, you preserve the document’s story. This makes it easier for anyone (clients, internal teams, or external counsel) to see what has changed over time. Inline or ‘balloon’ (our preferred method) comments further ensure each party can understand the rationale behind edits.
Clarity
One of the top goals in contract negotiations should be clarity. When you present the counterparty (or internal stakeholders) with a single redlined version:
- They immediately identify recent changes.
- They can refer back to older, accepted edits if needed.
- They see important comments and open questions without having to hunt through separate documents.
- You can ask your internal stakeholders specific questions, which they can resolve in the same document.
4. When (and How) to Use Compares
Validate Your Changes Internally
Even if you prefer to continue in the same redlined doc, a document compare can still be incredibly valuable for quality control – especially in multi-stakeholder negotiations. What happens often in negotiations is that two lawyers lead the negotiation, but they ask input from various specialists like experts in data privacy, tax, data security, product, intellectual property etc.
Before circulating a “new” version externally, run a compare on your own to ensure you haven’t accidentally skipped anything or misapplied a request from the other side. This step helps catch:
- Missed revisions or hidden text changes.
- Accidental deletions or additions that no one noticed.
- Formatting or numbering issues that might cause confusion later.
Provide a Compare Alongside the Redline in Complex Deals
In more complicated deals where multiple stakeholders (e.g., finance, technical, local counsel in different jurisdictions) are editing the same draft:
- Stick to One Master Redline – Everyone tracks changes in the central Word document.
- Create a Compare Version (at Key Milestones) – If your CFO, the counterpart or external counsel only wants to see what’s new since the last milestone, you can provide a compare word file or PDF (as a matter of exception) in addition to the main redline.
Tip: Communicate why you take this extra step.
5. When (and Why) to Use or Avoid Extra PDFs
At first glance, PDF redlines can seem like old-school overkill. Why not stick to Word track changes? But in certain cases, like when working with large law firms or complex finance and corporate deals, PDFs are not only accepted but often expected.
Let’s dive into the “mobile-viewing” and “Locked Compare Can’t Be Accidentally Edited” rationale driving PDFs.
The Mobile-Viewing Argument
Some lawyers say they send PDFs because executives often review contracts on smartphones – and a PDF might be easier to read on mobile. While there’s some truth to that, it usually doesn’t justify an entire multi-step PDF approach for each iteration. Instead:
- Ask your client or opposing counsel if they truly need a PDF on every turn.
- If necessary, just export your tracked Word doc to PDF, maintaining comments and highlights.
A Locked Compare Can’t Be Accidentally Edited
Another reason some teams stick to PDFs is that a PDF compare can’t be inadvertently altered, unlike a Word-based compare that might be changed by mistake. To be honest, I have seen this happen more than once in a large negotiation with many parties involved.
This “locked” snapshot can be reassuring for large finance or corporate transactions—especially when multiple parties are scrutinizing each version. However, even this benefit doesn’t mean you need a separate PDF for every round of edits.
In most commercial negotiations, a single redlined Word doc plus occasional internal compares is enough. Extra PDF compares can be saved for big milestones or final checks.
Potential Downsides of Separate PDFs
- Loss of Comments: Often, inline comments are not as interactive in PDFs. They do not work as well as comments in Word.
- Extra Steps: You spend more time saving, comparing, and formatting multiple files.
- Reduced Collaboration: PDFs limit the recipient’s ability to directly edit or reply in real time.
- Confusion: especially business people (sales, executives, etc.) might be confused why separate documents are sent and questions arise which document to review or amend.
6. How Legal Tech and AI Can Simplify Redlining
A straightforward way to tackle many redlining headaches is to turn to Legal Tech – particularly Contract Lifecycle Management (CLM) platforms and AI-powered solutions. See this article from Krysta Johnson on this subject for example. Below is a quick look at how these tools can streamline your negotiation process:
Key Benefits of Modern Legal Tech
- Centralized Dashboard
Keep contracts, edits, and comments in one place. No more searching for scattered files or wondering which version is current. - Automated Workflows
Easily ping the right teammates or approvers when it’s their turn. Once they’re done, their feedback is automatically saved and organized, cutting down on email clutter. - Smart Document Comparison
AI can quickly scan and highlight every edit between drafts, minimizing the risk of missing hidden changes or problematic clauses. This frees you to focus on actual deal issues rather than manual proofreading.
Bottom Line: By integrating CLM and AI into your redlining workflow, you’ll reduce manual effort, eliminate confusion, and speed up contract negotiations. This brings the team together to focus on what truly matters: reaching a solid, mutually beneficial agreement.
7. Nada Alnajafi’s 10 Steps for Transparent, Efficient Redlining
To illustrate how a seasoned contracts professional redlines documents in a way that promotes transparency, efficiency, and collaboration, Nada Alnajafi (Founder of Contract Nerds and author of Contract Redlining Etiquette ) has identified 10 key steps in this LinkedIn post. She emphasizes that this framework is backed by real data from thousands of contract professionals, not just personal preference:
Key Points
- Start in Word: Open the counterparty’s redlines in Microsoft Word to keep everything in one editable format.
- Get the Big Picture: Skim the draft from start to finish for an overview of the level of disagreement and the other side’s negotiation style.
- Dive Deeper: Review the document thoroughly to identify areas needing attention, extra discussion, or stakeholder input.
- Accept & Resolve: Accept any edits you agree with and resolve closed comment threads to keep the document uncluttered.
- Reject & Propose: For edits you disagree with, reject the changes, propose new language, and add comments explaining your stance.
- Ask Questions: Seek clarification for any unclear edits—better to ask now than to assume incorrectly.
- Consult Stakeholders: For business or commercial changes, loop in your internal teams or relevant departments.
- Summarize Top Issues: When sending your redlines back, highlight the most critical (no more than three) items in a short cover email.
- Request a Call if Needed: If major disagreements persist or time is short, a quick conversation can resolve more than endless markup rounds.
- Verify Before Signing: Run a single doc compare of the original draft vs. the final draft to confirm no hidden changes. Doing it more than once often adds unnecessary friction—especially in an in-house environment.
Nada’s final reminder is that one thorough compare is usually enough. If you repeatedly scrub redlines or generate “clean” versions out of fear or distrust, you risk delaying the process and frustrating everyone involved. For more contract redlining efficiency tips, be sure to check out her book Contract Redlining Etiquette and follow her on LinkedIn.
8. Final Takeaways
The Balanced Approach
- Keep a Single Redline: Work in one main track-changed document, accepting or rejecting changes as deals progress.
- Add Comments: Use inline comments to clarify reasoning or ask questions; this preserves context.
- Run Your Own Compare: Internally verify major new versions against the prior version before sending.
- Consider Sending a Compare: For complicated multi-stakeholder deals, provide a separate compare doc at key milestones, but don’t make it your default for every tweak.
- Avoid Unnecessary PDFs: Unless it’s truly required or requested, do not to use the PDF-based workflow.
- Use Legal Tech & AI: If you’re dealing with many contracts or looking to scale your process, consider specialized tools that streamline workflows.
- Meet in Person: For overly complex or stalled negotiations, a face-to-face (or online) meeting often resolves issues faster than endless redlining.
Why It Matters
- Client-Focused: Clients want clarity, results, and efficiency. They do not want to pay for avoidable drafting detours.
- Reduces Errors: A single doc plus strategic compares minimizes the risk of losing track of changes.
- Saves Time: Keeping everyone focused on one version speeds up reviews and shortens negotiation cycles.
Next Steps
- We advise to move away from the complicated 6-step approach and adopt a single, continuously updated redline with occasional compares.
- For more complex deals, use a hybrid approach: keep a master redline, but generate compare outputs at critical moments in the negotiation.
- Invest in training: Ensure your team is comfortable with Word’s Track Changes, Comments, and Compare features so that everyone contributes to a smooth, transparent workflow.
9. Ready to Streamline Your Redlining?
Contract negotiation doesn’t have to be a complicated (e.g. by using multiple PDFs and “clean” Word files). By adopting a continuous redline strategy—with optional compares as needed—and communicating expectations from the start, you’ll improve transparency, reduce costly errors and keep your clients or business stakeholders happy. Whether it’s an NDA, SaaS agreement or a complex M&A transaction, focusing on one document as your “source of truth” can make all the difference.
Need help? Contact me at rreggers@amstlegal.com or read our blogs for more about efficient negotiation tactics, ways to speed up contract processes and specific contract advice (e.g. relating to NDAs and SaaS contracts). We will work with you to develop a faster, more reliable approach that benefits everyone involved in the deal – based on our 20+ years of experience, aligned with industry-proven methods.

Negotiation Skills to Focus on at the End of Year
At the end of the year, many businesses rush to finalize contracts, close important deals and meet last-minute deadlines. Having great contract negotiation skills are essential to be successful. It’s that annual push to finish the quarter & year strong before everyone disappears for well-deserved time off. This pressure often falls heavily on legal teams, procurement, sales managers and business leaders tasked with ensuring that high-priority contracts are negotiated and completed on time.
In this article ‘Negotiation Skills to Focus on at the End of Year’, we will explore holiday rush negotiation tips for succeeding at the end of the year to close contracts. Also see this article with more tips to prepare for the end of year rush in contract negotiations.
We will highlight four essential actions you can take right now, just days before the holidays, to effectively wrap up your end-of-year deals. We’ll also walk through key fundamentals to keep in mind throughout the year so that next holiday season feels less chaotic. No matter how much experience you have, we are sure that these practical tips will help you for successful year-end deal closings.
What we will cover:
- Prioritize crucial contracts.
- Maintain transparent communication with internal and external teams.
- Foster cross-team collaboration.
- Manage deadlines effectively.
Let’s dive in.
Why the End of the Year Can Feel Overwhelming When Involved in Contract Negotiations
For many organizations, the fourth quarter (Q4) is do-or-die time. Sales targets loom, and finalizing deals before the calendar flips can make the difference between achieving annual revenue goals and falling short. Meanwhile, everyone is juggling personal holiday plans, limited workdays and company events. All of this can your timelines and add complexity to negotiations and sign-offs.
It’s important to acknowledge this heightened intensity and plan accordingly. What often appears as a mere scheduling inconvenience may result in real losses if a signature doesn’t come through before December 31st. With limited business days left in the year, how can you maximize efficiency and productivity without losing sanity?
Looking Ahead: Contract Negotiation Fundamentals for a Less Stressful End of Year
Before we get into the four actions to take this week, let’s talk briefly about the broader fundamentals. If you can keep these 4 foundational pillars in mind throughout the year, you won’t be scrambling at the last minute next time.
1. Early Preparation and Prioritization
One of the best ways to avert holiday panic is by starting your contract prioritization well before December. In contract negotiations, if you treat every contract as urgent in the final weeks of the year, you will get stuck. Begin categorizing contracts by priority as early as Q3, identifying which are mission-critical and which can be safely pushed to the new year. For further tips on how you can set your team up for success, read this article here.
Actionable Steps for Better Preparation
- Create a rolling calendar: Outline all major deals and renewal deadlines. Update it monthly to keep everyone informed.
- Rank your deals: Use clear metrics (like projected revenue, strategic importance, or executive sponsorship) to determine which contracts are must-close.
- Build buffer time: Aim to finalize deals a week or two before the official holiday break. If last-minute changes occur, you’ll have a cushion.
2. Communication & Cooperation
As we discussed in this previous article, improved cooperation and communication will speed up legal processes and contract negotiations. Encourage an environment of open dialogue and teamwork from the start. Legal, sales, finance and procurement should be in sync on timelines and requirements.
Throughout the year, there should be trainings and teams should have frequent check-ins to help keep everyone aligned on strategies, improvements and cross departmental input. When the end of the year crunch time arrives, you’ll already have established rapport and processes to move swiftly.
Actionable Steps for Ongoing Cooperation
- Weekly or bi-weekly alignment calls: Keep relevant departments in the loop on contract statuses and expectations.
- Transparent pipeline reporting: Make sure sales forecasts are accessible to the legal team, so there’s no surprise rush in December.
- Encourage feedback loops: If an issue arises, escalate it early rather than waiting until the last few days.
- Training: departments should give training to each other during the year understand products, processes and priorities.
3. Standard Templates
As we have explained in previous articles (like in this article here), setting up standard templates and clause libraries for routine contracts can save time and makes all the difference. If everyone works from the same template and standard pre-approved clauses, contract negotiations focus on key points rather than re-inventing the wheel every time.
Actionable Steps to Streamline with Templates
Three actions you can take take to improve your templates and to ensure that the team is actually using the templates are:
- Audit current contracts: Identify recurring clauses or sections across multiple deals.
- Implement version control: Store templates in a central, cloud-based location.
- Train stakeholders: Give internal teams a brief tutorial on how to use and customize the templates for common scenarios.
4. Implementation of Legal Tech & AI
Investing in Contract Management or Contract Lifecycle Management (“CLM“) and AI tools or other legal technology drastically speeds up contract negotiations, redlining and approvals.
What I particularly like is – if you have the right tool – that all contracts are handled centrally and are not scattered in the company. These tools can also automatically flag unusual terms, propose alternative wording, track changes and integrate e-signatures, reducing the manual workload.
Actionable Steps to Embrace Legal Tech
- Start small: Pilot a CLM tool on a specific contract type or business unit.
- Track ROI: Monitor how much time you save using automated workflows.
- Scale up: Gradually expand the tool’s usage across departments once it’s proven effective.
Pro-Tip: Implementing these fundamentals early in the year pays off when you hit the December crunch.

Four Actions to Take This Week in Your Contract Negotiations (Yes, You Still Have Time!)
Now that we’ve covered the broader, year-round strategies, let’s zoom in on the actions you can take right now to improve your contract negotiations – four days before the end-of-year holidays. It’s crunch time, but with a methodical approach, you can still cross the finish line successfully. Also see this article about how to get contract signed successfully before the holidays periods here.
1. Prioritize High-Value Q4 Deals
Why it Matters:
Time is limited, so focus on the deals that actually must be negotiated and close before the holiday break. Not every contract currently on your desk is critical for year-end. Some might realistically belong to Q1 or Q2 of the coming year – postpose the contract negotiations to that time..
Key Question to Ask:
“Is this contract truly closing before the holidays, or can it wait until Q1 ’24?”
If it’s not high-priority, schedule it for a later review. Redirect your energy toward the deals that can realistically be finalized. This ensures you’re not losing energy on deals that don’t directly impact your Q4 numbers.
Action Steps
- Identify urgent deals: Compile a list of deals that must be signed by December 31st.
- Eliminate the noise: Put lower-priority contracts on the back burner until after the new year.
- Communicate priorities: Let your internal stakeholders know which contracts you’re prioritizing, so they don’t assume everything is a must-close.
Check:
- Are the contracts you’re spending the most time on truly the ones that align with your company’s Q4 goals?
- Have you clarified the timing of the contract negotiations with the sales and management teams?
2. Establish Clear Communication Channels in Contract Negotiations
Why it Matters:
Poor communication can derail even the simplest deal. With holidays looming, there’s no time for back-and-forth email delays or misunderstandings. Clarity on timing, process, and expectations keeps everyone accountable- it is part of any good contract negotiation.
Key Question to Ask:
“Do my customers and internal teams fully understand the timeline and process, or are they making assumptions?”
If everyone is on the same page, you’ll drastically reduce the risk of any last-minute surprises. Communication is especially crucial with external customers. They may have their own holiday schedules and organizational processes that can cause bottlenecks if not carefully managed.
Action Steps
- Daily touchpoints: If a deal is critical, schedule short daily check-ins (virtual or in-person) with key stakeholders.
- Transparent timeline: Document the final date to submit revisions, secure approvals, and obtain signatures. Share this timeline widely.
- Preempt obstacles: Ask your counterpart, “What could prevent us from signing this on time?” Address those issues immediately.
Check:
- Are your internal teams (legal, finance, sales) updated on each contract’s status daily?
- Do your external customers have a complete understanding of the steps needed to finalize the contract?
3. Foster Cross-Functional Team Collaboration
Why it Matters:
No complex contract closes in a silo – contract negotiations are a team sport. The legal team needs sign-offs from finance and management. Procurement might require additional approvals from leadership. Sales might need input from marketing. Silos create delays, confusion, and errors—especially when deadlines are tight.
Key Question to Ask:
“Am I getting stuck in the details that create delays, and could a quick internal phone call solve it?”
Avoid working in isolation on complicated terms. Pull in all relevant parties for a collaborative push. If something is unclear or contested, schedule a call. The final week of the quarter isn’t the time for elongated email threads. Focus your time on live contract negotiations. See our tips on these live negotiations here.
Action Steps
- Set cross-department meetings: In the last crunch, a 15-minute daily huddle can resolve issues faster than back-and-forth emails.
- Draft clear escalation paths: Decide in advance who has the authority to sign off or escalate if disagreements arise.
- Leverage technology: Real-time collaboration tools (e.g., shared contract portals, Slack channels) can provide instant updates.
Check:
- Is everyone who needs to approve or review a contract looped in early enough?
- Do you have a protocol for addressing high-level disputes or changes quickly?
4. Execute Deadline Management Rigorously
Why it Matters:
Missing a critical date or a necessary signature in the last week of Q4 can be the difference between success and failure. Year-end deadlines often come with little to no grace period. If the contract doesn’t close by December 31st, it likely moves to next year’s pipeline – impacting revenue targets and stakeholder expectations.
Key Question to Ask during Contract Negotiations:
“What are the exact steps needed for this contract to be executed by the deadline?”
List those steps—from last-minute edits to final legal approvals to e-signatures—and align your timeline with all decision-makers. Don’t forget about the logistics of traveling or out-of-office signatories. One absent signature can delay everything if not planned for.
Action Steps
- Create a master checklist: Outline every step required for each contract (legal review, internal approvals, signature scheduling).
- Plan a few days ahead: Don’t assume you can finalize everything at the stroke of midnight on December 31st. Aim to have signatures done at least a few days before the holiday break.
- Leave room for error: Build in buffers for unexpected events like system downtime, signatory travel, or additional negotiation points.
Check:
- Has every individual with signing authority confirmed their availability before the holidays?
- Are you proactively tracking each contract’s progress against a unified timeline?
Putting It All Together: A Roadmap for the Final Week of Negotiations
With the holiday clock ticking, your best moves are laser-focused prioritization, great communication between teams , collaborative teamwork and tight deadline management.
By combining these actions over the next few days, you’ll massively improve your odds of wrapping up critical deals. Remember to keep an eye on the fundamentals – early preparation, open communication, standardized templates and legal tech—so that next year, your holiday season won’t feel like a marathon sprint.
Bonus Tips for a Smoother Year-End Experience
Even if you have just a few days left before the break, here are some bonus strategies to make your life a bit easier:
- Use E-Signature Solutions: If you haven’t already, adopt an e-signature platform. Paper-based signatures in the final days can lead to shipping delays or the dreaded “I’m on vacation, I’ll sign when I’m back” scenario.
- Send (Early!) Friendly Reminders: People get distracted this time of year. A polite nudge via email or chat can keep deals top of mind.
- Confirm Receipt: After sending over final documents, confirm your counterparty has received them and is working on them. Sometimes emails get lost or stuck in spam.
- Celebrate Small Wins: For every contract closed, give your team credit. Positive reinforcement keeps morale up as you sprint toward the finish line.
- Prepare for Post-Holiday Catch-Up: Not every deal will close on time, no matter your best efforts. Have a plan ready for picking up negotiations in January without losing momentum.
Conclusion: Good Luck Closing Off Your Contracts Before the Holidays!
End-of-year contracting is not easy and it will be messy. Hopefully these tips will help you – which I pulled together in the past 20 years – trying to minimize the chaos at the end of each year. By prioritizing deals, clearly communicating, collaborating effectively and managing deadlines meticulously, your deals will close easier and with less stress.
Remember: The core pillars we discussed at the start – early preparation, cross-functional communication, standard templates & procedures and use of legal tech form the bedrock of a less stressful contract negotiation and management process. Implement them gradually, and you will notice a smoother Q4 (and end of Q2) next year. For even more detailed advice, be sure to check out our comprehensive guide here.
Good luck, and may your holiday season be filled with both successful deals and well-earned relaxation!
Need help?
For help with your contract negotiations and related processes, reach out to us via info@amstlegal.com or book an appointment with Robby Reggers here.

7 Tips How to Improve Live Contract Negotiation (&Examples)
Introduction
Long, drawn-out live contract negotiations where you don’t reach a result can drain your time, energy and patience. Whether you’re finalizing terms with a new SaaS vendor or ironing out details with a new customer, the process often feels slow and frustrating. But it doesn’t have to be this way.
By applying a few straightforward communication and contract negotiation strategies, you can streamline your live (online or in-person) negotiations, keep everyone focused and reach fair agreements faster. In this article ‘7 Tips How to Improve Live Contract Negotiation (& Examples)’, we will cover:
- seven tips to help you run more efficient live negotiations,
- then, answer five common questions that many small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs) have asked us; and
- finally, we’ll walk through a brief scenario showing how these tactics work in a real-world SaaS context.
7 Tips for More Effective, Streamlined Live Negotiations
1. Prepare in Advance
Preparation might sound obvious, but it’s often overlooked. Before you jump on a call, know exactly what you want—and what you can live without. Gather all the details that matter: pricing tiers, subscription lengths, service-level agreements (SLAs), data security requirements, and any key terms unique to your business model.
For instance, if you’re negotiating a SaaS contract, determine your must-have SLA features (like 99.9% uptime or a dedicated support channel) and understand how much you’re willing to pay for them. Knowing these details ensures you’re not scrambling during the call. You’ll respond faster to counteroffers and will not waste time on irrelevant points. The clearer your objectives, the quicker you can confirm or reject proposals on the spot.
To prepare effectively for our live negotiations, prepare thoroughly. Review your internal needs, compare the vendor’s standard terms to industry benchmarks and decide where you can compromise. Also, anticipate common sticking points – like automatic renewal clauses or extra fees for additional users – so you’re ready to address them. Thorough preparation reduces confusion and sets the stage for a focused, productive negotiation.
Be ready for the tough questions. See the Harvard Law School Negotiation preparation checklist here.
2. Set an Agenda and Stick to It
Without a clear roadmap, negotiations can meander and waste time. A simple agenda shared in advance keeps everyone aligned. List the key issues—such as pricing structure, onboarding timeline, renewal conditions and data protection terms – and let all parties know these are the topics to be covered.
When the call starts, refer to the agenda right away. If someone drifts off-topic (“Let’s also discuss a potential partnership feature for next year…”), you can steer them back: “That’s interesting, but let’s finalize the current subscription terms first as per our agenda.”
An agenda not only saves time but also keeps the atmosphere professional and respectful. Everyone knows what to expect, which reduces unnecessary back-and-forth. With a clear roadmap, you’re less likely to get bogged down in small details that don’t affect the final outcome.
3. Use Clear, Concise Language
Complex legal or business jargon and vague language can slow negotiations down. Stick to plain, direct language whenever possible. If you encounter a technical or legal term, clarify it right away. For example, if the vendor refers to a “Indemnification Clause” or “SLA” ask them to explain: “Can you clarify what this clause means in practical terms for our liability and what exactly the SLA will entail?”
By simplifying terms, you ensure both sides understand each other. Misunderstandings often lead to follow-up calls or extra email chains to fix what could have been settled earlier. Keep it simple: “We need a 48-hour response time for support tickets” is clearer than “We request timely fulfillment in accordance with standard SLA metrics.” Clear language reduces confusion, makes it easier to achieve agreement and speeds up the entire process.
Also, don’t just refer to a contract clause, memo or whitepaper that was shared, but explain in your own words.
4. Assign Roles and Responsibilities Within Your Team
If you have several team members on your side, assign clear roles before the call. One person should lead the conversation – this is the voice who guides the agenda and addresses the main points. Another can handle real-time edits to the contract (if you’re screen-sharing or using a collaborative doc), ensuring that agreed-upon changes are captured immediately. A third team member might be a specialist in a particular subject, etc.
This division of labor prevents people from talking over one another and ensures nothing falls through the cracks. For example, while the lead negotiator discusses the price tiers with the vendor, the notetaker can record the agreed terms, and the editor can update the master document in real-time. When everyone knows their role, the conversation flows smoothly. By the end, you’ll have a clear record of what happened and fewer reasons to schedule a second call.
When you know a particular point could be sticky, ensure that you have a specialist that joins the call to show your willingness to explain and to try yo reach agreement on the spot. Before the meeting, also ask the counterparty if their specialist is able to join so they can discuss the specific subject.
5. Actively Listen, Ask Great Questions and Validate the Other Side’s Points
Negotiations aren’t just about what you say; they’re also about how well you listen. When the other side speaks, give them your full attention. Summarize their points to show you’ve understood: “Great to hear that if we agree to sign a two-year contract, we will receive a 10% discount.”
By validating their input, you build trust and minimize friction. The other side feels heard and respected, making them more open to meet you halfway. If a vendor says they can’t offer more storage at the basic tier, acknowledging their position – “I hear you. Additional storage is challenging at this price point” – can calm tensions and open the door to creative solutions.
Don’t for get the tip to say “That’s Right” when your counterpart makes a great point. Read our article about this here.
Active listening also helps you avoid going in circles. When everyone feels understood, fewer clarifications are needed later. It’s a subtle step that speeds up the process by preventing repeated explanations or misunderstandings. Also see our article ’30 of the Best Questions to Ask in Any Negotiation’ here.
6. Leverage the Right Technology
The right tools can save a lot of time in negotiations. For example screen-sharing allows both sides to view and edit the contract simultaneously. Collaborative documents or contract management platforms let you highlight text, propose changes, and record agreements as they happen. Real-time chat tools can clarify small points without derailing the conversation flow.
Let’s say you are discussing a SaaS license agreement, you can highlight the pricing clause live, increase the user count and watch the other side’s response in real-time. This eliminates the need for lengthy email follow-ups after the call. Technology also helps ensure everyone is literally “on the same page,” reducing miscommunication and speeding up finalization.
Just remember to test your tools beforehand. Technical glitches waste time and damage the negotiation’s momentum. Ensuring everything runs smoothly keeps the process moving and makes it easier to reach an agreement.
7. Know When to Take a Break
Sometimes you hit an impasse. Maybe the vendor won’t budge on a crucial data security or liability clause or you can’t agree on cancellation terms. Instead of pushing on and raising tensions, suggest a short break: “Let’s take five minutes to review these points individually. We’ll come back with fresh perspectives.”
Stepping away from the screen allows everyone to rethink their positions. When you return, both sides might be more willing to compromise. A brief pause can save you from hours of drawn-out debate. Instead of forcing a decision amid rising frustration, you come back calmer and more solution-oriented, ultimately reaching an agreement faster.
5 Common Questions (and Answers) About Live Negotiations
1. How do I handle a party that dominates the conversation?
Use your agenda to maintain structure. Politely interrupt if they wander off: “I appreciate your input. To stay on track, let’s confirm the billing cycle terms first.” If dominance persists, consider switching negotiation formats, like proposing a written redline exchange before the next call. This allows for more balanced input and prevents one-sided monologues.
2. What if I don’t understand a technical or legal term they mention?
Ask for clarification immediately: “Could you clarify what this ‘auto-renewal clause’ entails?” A moment of asking now saves you from bigger problems later. Being upfront about what you don’t know shows professionalism and ensures no hidden surprises remain after signing.
3. How do I keep everyone engaged and focused?
Start by setting a time target: “We have one hour to finalize the user limits and support terms.” Recap progress after each point: “Great, we agreed on a 12-month term at $X per month. Next, let’s finalize the onboarding schedule.” Timeboxing and summarizing key decisions keep the conversation efficient and participants engaged.
4. What if I feel pressured to accept unfavorable terms just to end the call?
Acknowledge the urgency without conceding too quickly: “I know we’re close to wrapping up, but I need a moment to confirm these terms align with our internal policies.” Suggest a brief pause or a follow-up call if needed. It’s better to take a bit more time now than sign a bad deal you’ll regret later.
5. How can I ensure the terms agreed upon are actually implemented afterward?
End the meeting by summarizing important agreed terms, who is responsible for what and the next steps. Then send a written summary email or updated contract draft immediately after. Having a document both sides can refer to prevents “he said, she said” disputes and keeps everyone accountable for their promises.
A Quick Scenario: Negotiating a SaaS Contract in Live Negotiations
Imagine you run a growing marketing agency, and you’re negotiating a SaaS contract for a new project management platform. You’ve done your homework: you know your budget, the required user count, must-have integrations (like linking to your CRM), and the level of customer support you need.
Preparation:
Before the call, you decide that you need a minimum of 30 seats at a certain monthly rate. You also need a guaranteed response time for support tickets, integration with your CRM, and a flexible cancellation clause.
Agenda:
You send the SaaS vendor a short agenda:
- Pricing and number of seats
- Support response times and escalation policies
- Integration with CRM tools
- Cancellation and renewal terms
Clear Language:
On the call, you say, “We need at least 30 seats at $X per user per month, with a guaranteed 24-hour support response time. Can you confirm that’s possible?” This straightforward request helps the vendor respond faster. They might say, “We can offer 30 seats at that rate, but our standard support time is 48 hours.”
Assigning Roles:
In your team, you’re the lead negotiator. Your colleague is ready to update the shared Google Doc with any changes. Another teammate listens and takes notes on agreed points. While you talk pricing, your colleague highlights the relevant clauses in the contract so everyone can see what’s changing.
Active Listening:
The vendor expresses concern about meeting the 24-hour support response. You summarize: “You’re saying 24 hours might be tight. How about 36 hours as a compromise?” This shows you listened and are open to meeting them halfway.
Leveraging Technology:
As you discuss these terms, you screen-share the contract. Your teammate edits the pricing clause and support terms in real-time. Everyone sees the new wording instantly. No follow-up emails are required later to confirm what was changed. Additionally, if you have shared the document in your organization (Google Docs or Onedrive for example), you can ask questions to other team members by adding a comment and tagging them.
AI use: while negotiating certain, open legal AI tool (Harvey, Legora, GCAI) to amend or add clauses or definitions. This will greatly speed up reaction time regarding the amendment or addition of certain clauses
Taking a Break:
If you reach a deadlock. For example, I asked for a short break when the vendor wanted a strict auto-renewal clause where we preferred a more flexible cancellation policy. Another option can be to take a break when a derogatory remark was made during a call. “Let’s take five minutes so we can consider some options.” After the break, you might propose a partial compromise: a 30-day cancellation notice instead of 60 days. The vendor, now calmer, might agree.
By the end of the call, you summarize: “We’ve agreed on 30 seats at $X per month, a 36-hour support response, full CRM integration within 30 days of signing, and a 30-day cancellation notice. I’ll send an updated contract draft today, and you’ll review it by Friday.” Sending that draft immediately seals the verbal agreement in a written form, reducing any risk of confusion.
Building Confidence Over Time in Live Negotiations:
These tactics become easier the more you use them. After a few live negotiation sessions, you’ll know when to push back, when to pause, and how to keep the conversation clear and constructive. Over time, refine your agenda templates, prepare standard clauses, and train your team to handle their roles seamlessly.
Improving your negotiation approach doesn’t just save time. It also helps maintain positive relationships with vendors and clients, who appreciate smooth, respectful interactions. Everyone wins when deals close faster and with less friction.
Also, don’t forget to check out our list of negotiation Books to read to become a better negotiator.
Conclusion:
Long live negotiations where you reach no results don’t have to be your standard. By preparing in advance, setting a clear agenda, speaking plainly, delegating tasks within your team, listening closely, using the right tools, and knowing when to step back, you can drastically shorten negotiation times and reduce stress.
This structured approach leads to fairer deals struck in less time. Instead of hours or days spent ironing out small details, you’ll wrap up contracts more efficiently. You’ll protect your interests and keep your partners happy, setting the stage for productive, long-term relationships.
Need help?
For help with your contract negotiations and related processes, reach out to us via info@amstlegal.com or book an appointment with Robby Reggers here.

9 Actions to End the Year Strong in Contract Negotiations
Introduction
As the end of Q4 2024 approaches, legal and commercial teams face pressure to finalize contracts before the holiday break. The final weeks of the year present unique challenges, with tight deadlines, competing priorities and holiday disruptions. Success depends on aligning your team and prioritizing the most critical contracts with a focus on maintaining clear communication throughout the process.
With 20 December 2024 as the (most likely) last day to finalize contracts, prioritizing deals that directly impact your company’s goals is essential. At the same time, addressing dormant deals and preparing for next year when time allows will ensure a smooth transition into 2025.
What We Will Cover in This Article
To finish the year strong and enter 2025 with momentum (while feeling rested), you need to focus on the following now:
- Bring your teams together to align on priorities and processes.
- Devote your full attention on clear communication, both internally and with customers.
- Prioritize Q4 2024 deals, address dormant contracts and prepare Q1 2025 deals if time permits.
In this article, we will outline 9 actionable tips to help you organize your efforts, streamline workflows, and avoid a year-end scramble.
9 Actions to Close Out the Year Successfully
1. Align Priorities Across Teams
The first and most crucial step is to bring all relevant teams together—Legal, Sales, Procurement, and Operations. Without alignment, resources can be wasted, and critical deals may slip through the cracks.
- Host Priority Meetings: Convene key stakeholders to discuss active contracts and set clear priorities.
- Set Realistic Timelines: Share anticipated closing dates and deadlines, taking into account holiday schedules.
- Address Bottlenecks Early: Identify potential obstacles, such as approvals or customer feedback, and plan to resolve them.
- Document Priorities: Create a shared list of deals and communicate expectations to all involved.
Why This Matters: A lack of alignment leads to confusion and delays. Clear communication ensures everyone is working toward the same goals.
2. Finalize Q4 Deals That Matter
After aligning priorities, focus your efforts on closing Q4 2024 deals that are most important to your company’s financial and strategic objectives. These contracts often involve high-value agreements or partnerships where delays could have serious consequences.
- Assign dedicated resources to critical deals.
- Regularly update internal and external stakeholders on progress.
- Use the tools and processes your company has designated for tracking and approvals.
Key Question: Which deals are tied to year-end financials or essential company objectives?
3. Prioritize High-Value Deals
Within the Q4 pipeline, high-value deals deserve special attention. These agreements often require more complex negotiations, multiple approvals, or input from senior decision-makers.
- Set weekly check-ins with deal teams to track progress.
- Identify potential risks or delays early and create contingency plans.
- Ensure executive stakeholders are available for final approvals.
Why This Matters: High-value deals typically have the greatest impact on your company’s year-end performance and strategic goals.
4. Push Small Deals to Close Quickly
While high-value contracts demand attention, small deals should not be overlooked. These agreements are often easier to finalize and can contribute to year-end results with minimal effort.
- Set a goal to close smaller contracts early in December.
- Automate workflows where possible to speed up execution.
Why This Works: Small deals are low-hanging fruit that boost momentum and free up resources for larger negotiations.
5. Address Dormant Deals Immediately
Dormant contracts – those that you have chased but have not heard back from or are unresolved – should be reviewed and addressed now.
- Discuss and determine if these deals can be realistically closed before year-end.
- For contracts that cannot be finalized, communicate plans to defer them to 2025.
Key Tip: Don’t let dormant deals distract from critical Q4 priorities. Clear them out to create focus and clarity.
6. Communicate Proactively with Customers
Proactive communication is essential for keeping deals on track. Schedule touchpoints with high-priority customers to confirm timelines and address any outstanding issues.
- Share clear expectations for closing terms and deadlines.
- Follow up consistently to maintain momentum.
- Ask if certain specific closing requirements are important for the customer – for example signing protocols & timing.
Why This Works: Clear communication reduces uncertainty, builds trust, and helps avoid last-minute surprises.
7. Enable Your Team with Clear Instructions and Tools
Ensure your team has access to the right tools and a clear understanding of how to use them. This includes contract management systems, signing tools, and repositories.
- Save contracts in designated locations for compliance and easy access.
- Track progress on negotiations, approvals, and signatures using your company’s approved tools.
- Refresh your team on contract thresholds, policies, and escalation processes.
Why This Matters: Standardized workflows minimize confusion and ensure contracts are executed efficiently.
8. Review Processes, Not Just Contracts
A successful year-end close depends on streamlined workflows, not just finalizing agreements. Take time to review and address any gaps in your processes.
- Are all approvals aligned and documented?
- Have compliance requirements been met?
- Are decision-makers available for final signatures?
Why This Matters: Process inefficiencies can derail even the most well-negotiated deals.
9. Review Q1 2025 Deals Only If Time Permits
Finally, if your team has capacity, begin preparing for Q1 2025. Use this time to lay the groundwork for contracts that will need early attention next year.
- Draft templates and standard terms.
- Schedule initial meetings with stakeholders for early January.
- Address any known issues that could cause delays.
Key Tip: Keep your focus on 2024 until all critical contracts are on track to close.
Conclusion: Focus on What Matters Most
As the year draws to a close, success hinges on prioritization and clear communication. Focus your efforts on:
- Bringing your teams together to align priorities and streamline processes.
- Closing critical Q4 2024 deals that directly impact financial and strategic goals.
- Resolving dormant deals or deferring them to 2025 with a clear plan.
- Preparing for Q1 2025 only after year-end priorities have been addressed.
By following these steps and equipping your team with the right tools and processes, you can ensure a smooth year-end close and start 2025 with confidence.
We can also recommend a great article on this subject by Bari Williams, Head of Legal & Legal Content at LegalOn Technologies, see link on contractnerds.
For help with your contract negotiations and related processes, reach out to us via lowa@amstlegal.com or book an appointment with Robby Reggers here.

10 Tips You Need to Know to Improve Your Contract Templates
1. Introduction
Sales teams, entrepreneurs, procurement specialists and legal professionals all share one common need: contracts that are clear, efficient and enforceable. When done right, they accelerate deals, minimize risks and build trust. Contract Templates are great to achieve this.
These legal documents do not only formalize agreements but also protect business interests by clearly defining risks, responsibilities and expectations between the contractual parties. However, as important as contracts are, the process of managing them can be complex, time-consuming and inefficient.
The solution is standardizing contracts in templates. This can be in the form of template NDA’s, Custom Agreements, General Terms & Conditions, Master Services Agreements, Order Forms or even letters. The key is to create easy to use, not overly complicated (and short where possible!) templates that cover the company’s risk. A great practical book on this is ‘Sign Here: The enterprise guide to closing contracts quickly’ by Alex Hamilton.
Creating and maintaining strong, streamlined contract templates can help companies enhance efficiency, reduce legal risks and optimize resource allocation. Also see my article on this here. However, simply having templates is not enough. Organizations need to ensure that they are accessible, up-to-date and aligned with both legal and business objectives.
This article series, “10 Tips You Need to Know to Improve Your Contract Templates”, was written to help businesses tackle these challenges head-on. We will explore key strategies to improve contract templates, ensuring they become valuable tools that drive efficiency, consistency and strategic growth.
Let’s start by understanding why we need templates in the first place and how to overcome common issues that arise from their use. This Introduction article will be followed up by 10 more articles including a practical, step-by-step guide explaining how to improve templates, creating better processes and rolling them out successfully.
2. Why we need (better) Contract Templates
Companies need to work on avoiding overcomplicating contracts and to focus on improving contract workflows.
One effective way to achieve this is by creating standardized templates for the company’s most common agreements. For example, Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs), Terms & Conditions (T&C), Data Privacy Agreements (DPA), Service Level Agreements (SLA), Master Services Agreements (MSAs) etc.
Standardized contract templates can also significantly reduce the time spent on repetitive drafting. It enables faster contract creation, review, and approval, which not only speeds up business processes but also frees up valuable resources for more strategic tasks.
Moreover, contract templates help maintain consistency in the language, terms, and legal safeguards across all agreements, reducing the risk of errors, contradictory clauses, and legal disputes. By ensuring that key legal protections are consistently applied, contract templates minimize legal risks and contribute to more efficient, reliable contract management overall.
However, despite the clear benefits of using standard contract templates, many companies struggle with effectively implementing them. The correct use of these templates often remains a stumbling block, and failure to address common issues can lead to inefficiencies, delays, and legal risks.
In the next paragraphs, we will first highlight what the 4 most common issues are with Contract Templates, secondly what the consequences are of these issues, finalizing with explaining are the 9 advantages of having great (so not complicated & long) Contract Templates.
3. Common Issues with Contract Templates
While standardized contract templates can improve efficiency, many organizations encounter obstacles that prevent them from fully realizing their potential by using contract templates. In practice several factors can hinder the successful implementation and utilization of such contract templates.
Four of the most common issues with contract templates include the following:
Complexity
Overly complex and lengthy templates often result in confusion and create more questions than answers for the commercial team who use the templates in practice. The language may contain specific legal terms or overly complex wording, that can be difficult to comprehend, which in turn can slow down the contract review process. We also often spot that templates are outdated and no longer fit with the products & services that the company is providing.
Accessibility
Locating and using the correct template can be a challenge. The absence of a clear system for accessing the right templates often results in the use of outdated or unauthorized versions, creating further inconsistencies.
Limited Resources
Many businesses lack the resources to dedicate time to continuously improve their contract templates. This lack of investment often leads to templates that are outdated or irrelevant to current business needs.
Excessive Legal Review
Despite having templates in place, Legal often still need to review and negotiate a high volume of contracts due to the lack of well-defined processes and the issues mentioned above. This increases the burden on the Sales, Procurement & Legal department and slows down the contracting process.
The existence of these obstacles highlights the importance of having a clear strategy and process for managing contract templates. Understanding these common issues is a first step towards addressing them and ensuring smoother contract workflows.
4. Consequences of Contract Template Issues
The issues described above surrounding contract templates can have significant, far-reaching consequences for businesses in several areas. The idea of having solid contract templates in place relies heavily on whether the templates are easy to use, if they are consistent and whether they have been reviewed and continuously get managed properly. Mainly, this revolves around inefficiencies connected to the contract templates due to poor contract template management.
Incorrect, overcomplicated and long templates result in the following issues:
Delays in Contract Creation, Negotiation and Closing
Complex and outdated templates can prolong the time it takes to finalize contracts due to the need to involve legal professionals. If the template is too complex, it won’t be possible for anyone to use the template at issue. Additionally, this can cause delays that may disrupt operations and hinder business growth that otherwise would have been possible.
Increased Risk Exposure
Contracts that are inconsistent or not properly reviewed make the company vulnerable to legal and financial risks, including disputes, compliance issues, and unfavorable terms. This is especially the case if there are several contract templates that cover different areas.
Higher Workloads
The inefficiencies of managing contract templates translate to additional work for Legal and other involved departments. This means that they must spend more time resolving problems, negotiating terms, and handling unnecessary contract revisions since they are the only ones who are fit for the job. In turn, this creates less time for them to focus on more complex, high-value deals.
Strained Business Relationships
Poor contract management can also erode trust with clients, vendors, and partners. If the contracting process is slow, confusing, or fraught with errors, it can negatively impact business relationships and damage the company’s reputation. For instance, the counterparty can get the impression that the inconsistent templates may reflect your way of doing business.
In other words, the consequences of poorly managed contract templates extend far beyond operational inefficiencies. To prevent these issues, companies need to reassess their contract management strategies and prioritize the development of high-quality templates.
5. Results of having State-of-the-Art Templates
When businesses take the time to develop and maintain strong contract templates, they unlock a wide range of benefits that positively impact both their day-to-day operations and long-term strategic goals. These benefits arise from the ability to standardize contract processes, reduce legal risks, and enhance collaboration between departments.
Nine key advantages are:
Shorter Contract Negotiation Times
High-quality templates serve as a strong starting point for contract negotiations, eliminating the need to negotiate basic terms and conditions from scratch. Since most of the standard clauses are pre-approved and align with company policy, both parties can focus on customizing specific deal points rather than revisiting the entire contract.
Increased Efficiency and Simplified Contract Handling
Streamlined templates reduce the time and effort required to draft, review, and approve contracts. This reduces the administrative burden on both Legal and business teams, allowing them to focus on higher-value tasks such as negotiating complex deals or working on strategic initiatives. In fast-paced industries, this can provide a critical competitive advantage.
Reduced Workload
With standardized, well-organized templates, the Legal department can reduce the number of contracts that require individual review. This means that only the most complex or high-risk contracts will require in-depth legal review. It allows the Legal team to focus on more strategic activities, such as risk management or regulatory compliance.
Enhanced Consistency and Contract Quality
High-quality templates ensure that contracts across the organization are aligned with company standards, reducing the risk of errors and inconsistencies. Enhanced consistency also helps to build trust with external parties, as they can rely on the fact that the company’s contracts follow a predictable structure.
Risk Mitigation
Strong contract templates serve as a built-in risk management tool, ensuring that all agreements contain the necessary legal safeguards to protect the company’s interests. By ensuring that contracts contain the necessary legal safeguards and are compliant with applicable regulations, companies can better manage their legal and financial risks.
Decreased Legal Costs & Improved Cost Efficiency
With fewer contracts requiring in-depth legal review, companies can reduce their legal expenses and allocate their budgets more efficiently. This cost efficiency allows companies to allocate their legal budgets more effectively, focusing on complex matters that truly require expert legal input.
Stronger Business Relationships
A smooth and transparent contracting process enhances trust and collaboration with clients, vendors, and partners. It also reduces delays and confusion, making it easier to finalize agreements quickly and without unnecessary back-and-forth.
Optimized Resources
Well-organized contract processes help businesses make the most of their available human and financial resources. By standardizing and streamlining contract workflows, companies can minimize the time and effort spent on repetitive tasks, allowing teams to focus on strategic growth initiatives rather than administrative burdens.
Empowered Commercial Teams
With easy access to effective contract templates, commercial teams can take the lead in negotiations without the constant need for legal intervention. When teams have access to well-structured, pre-approved templates, they can confidently lead discussions and close deals faster.
In summary, adopting state-of-the-art contract templates into your business processes leads to a wide range of benefits. Not only do they increase efficiency and reduce legal costs, but they also improve the consistency and quality of your contracts. By streamlining contract workflows and fostering better business relationships, high-quality templates help companies mitigate risks, optimize resources, and accelerate growth. Implementing these templates is a smart investment that delivers long-term operational and strategic advantages.
6. Experienced Results of Contract Optimization
Throughout Robby Reggers’ 20-year career advising businesses on contract optimization within legal departments, the most successful outcomes were achieved by companies that embraced a collaborative methodology for template optimization. By refining contract templates with input from across the organization, companies can ensure that their contracts are not only legally robust, but also fully aligned with business objectives and responsive to customer needs.
For help improving contract templates, negotiations and related processes, reach out to us via lowa@amstlegal.com or book an appointment with Robby Reggers here.
